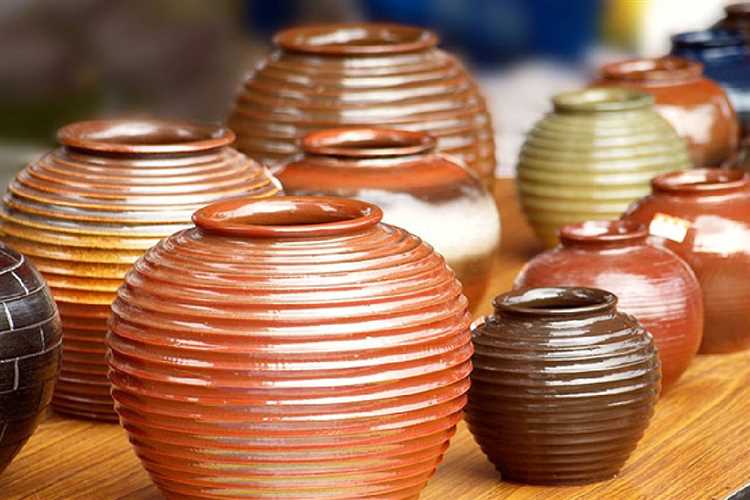
In the world of art and craftsmanship, the terms “pottery” and “ceramics” are often used interchangeably. However, there is a distinct difference between the two that sets them apart in terms of materials, techniques, and artistic purposes. While both involve the creation of objects from clay, pottery and ceramics have unique characteristics that define their individuality and significance.
Pottery, often associated with functional objects like bowls, plates, and vases, refers to the art of creating clay objects that are fired at relatively low temperatures. These objects are typically porous, making them suitable for holding liquids. The creation of pottery involves hand-building or forming clay on a wheel, followed by drying, glazing, and firing. As a result, pottery exhibits a more rustic and earthy aesthetic, emphasizing functionality over artistic expression.
Ceramics, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of clay-based objects, including both functional and non-functional pieces. Unlike pottery, ceramics are fired at higher temperatures, resulting in a dense and durable finished product. Ceramics can be hand-built or formed on a wheel, but they often involve more intricate techniques such as sculpting, molding, and carving. Furthermore, ceramics offer a wider artistic scope, allowing for experimentation with various glazing, coloring, and surface decoration techniques.
Overall, the distinction between pottery and ceramics lies in their intended use and artistic expression.
While pottery focuses on creating functional vessels, ceramics explore a broader range of artistic possibilities. From delicate porcelain sculptures to intricately designed pottery, the world of ceramics offers endless avenues for creative expression. By understanding the differences between pottery and ceramics, we can appreciate the unique craftsmanship and artistic traditions associated with each discipline.
Understanding the Distinction Between Pottery and Ceramics
Pottery and ceramics are often used interchangeably in everyday language, but there are actually significant differences between the two. While both involve working with clay and firing it in a kiln, pottery refers specifically to objects made from clay that is fired at a lower temperature, typically below 1200 degrees Celsius. Ceramics, on the other hand, encompasses a broader range of objects made from clay that is fired at higher temperatures, usually above 1200 degrees Celsius.
One key difference between pottery and ceramics lies in their intended use. Pottery is typically used for functional purposes, such as plates, bowls, and cups. It is often glazed to make it waterproof and food-safe. Ceramics, on the other hand, can be functional but are more commonly used for artistic or decorative purposes. They can take the form of sculptures, vases, or tiles, and are often left unglazed to showcase the natural beauty of the clay.
In terms of the clay used, pottery tends to use earthenware clay, which is lower-fired and more porous, while ceramics often use stoneware or porcelain clay, which can withstand higher firing temperatures and produce a denser, less porous finished product. The firing temperature also affects the final appearance and durability of the object, with pottery often having a more rustic and less refined look compared to ceramics.
Another difference between pottery and ceramics is the techniques used in their creation. Pottery is typically made using hand-building techniques, such as coiling, pinching, or slab construction, as well as wheel throwing. Ceramics, on the other hand, often involve more complex techniques, such as mold casting or slip casting, and may require multiple firings and glazing processes to achieve the desired result.
In conclusion, while pottery and ceramics share similarities in terms of working with clay and firing it in a kiln, there are distinct differences between the two. Pottery refers to objects made from lower-fired clay and is often used for functional purposes, while ceramics encompass a broader range of objects made from higher-fired clay and are more commonly used for artistic or decorative purposes. Understanding these distinctions can help to appreciate the unique qualities and characteristics of both pottery and ceramics.
The Origins of Pottery
Pottery is one of the oldest art forms known to mankind, with its roots dating back thousands of years. The origins of pottery can be traced back to various ancient civilizations, including those in China, Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece.
Many archaeologists believe that pottery was first created as a practical solution for storing and transporting food and water. The use of clay as a material for creating vessels allowed humans to store and preserve food for longer periods of time.
Early pottery was primarily hand-built, using the coiling technique. This involved rolling out long, thin coils of clay and then stacking them on top of each other to create the desired shape. The coils were then smoothed and blended together to create a solid vessel.
Over time, pottery techniques advanced, and potters began using the wheel to shape their vessels. This allowed for greater precision and consistency in the form of the pottery. The invention of the potter’s wheel revolutionized the pottery-making process and led to a significant increase in production.
In addition to its practical uses, pottery also played a significant role in religious and ceremonial practices. Many ancient civilizations decorated their pottery with intricate designs and motifs, often depicting scenes from mythology or everyday life. These decorative elements added beauty and symbolism to the vessels.
As pottery spread throughout different cultures, each civilization developed its unique artistic style and techniques. For example, the Chinese perfected the art of porcelain manufacturing, producing delicate and translucent vessels. In contrast, the Greeks excelled in creating large, ornamental pottery with intricate painted designs.
Today, pottery continues to be a beloved art form and is practiced by artisans all over the world. Modern potters have access to advanced tools and technology, allowing for even greater experimentation and creativity in their craft.
Overall, the origins of pottery are deeply rooted in the practical needs of ancient civilizations. From humble beginnings, pottery has evolved into a rich and diverse art form that has captivated people throughout history.
Techniques and Materials in Pottery Making
Pottery making is a versatile art form that involves various techniques and materials. Here are some commonly used techniques and materials in pottery making:
- Handbuilding: Handbuilding is a technique that involves shaping clay by hand. It can be done using different methods such as pinch pots, coiling, and slab construction.
- Throwing: Throwing is a technique where a potter shapes clay on a potter’s wheel. The potter spins the wheel while using their hands and fingers to shape the clay into a desired form.
- Glazing: Glazing is the process of applying a liquid glaze to the pottery. Glazes are made of a mixture of minerals and pigments that create a glass-like surface when fired at high temperatures. The glaze not only enhances the appearance of the pottery but also makes it more durable and waterproof.
- Firing: Firing is the process of heating the pottery in a kiln to harden and strengthen it. There are two types of firing: bisque firing and glaze firing. Bisque firing is the initial firing done before applying glaze, while glaze firing is done after the glaze application.
Pottery making involves the use of various materials, including:
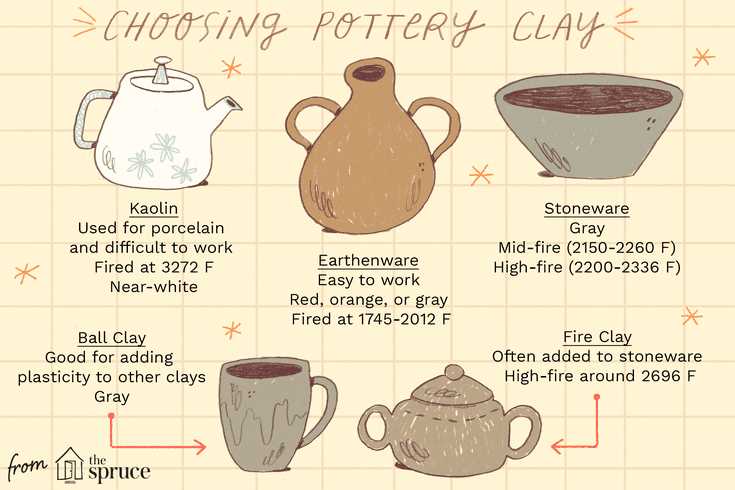
- Clay: Clay is the primary material used in pottery making. It is a malleable substance that becomes hard and strong when fired. Different types of clay, such as earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain, have different properties and are suitable for different types of pottery.
- Tools: Pottery making requires a variety of tools. Some commonly used tools include pottery wheels, kilns, clay sculpting tools, brushes for glazing, and clay cutters.
- Glazes: Glazes are an essential material in pottery making. They are available in various colors and finishes and can be used to create different effects on the pottery’s surface.
By employing different techniques and using a variety of materials, potters can create unique and stunning pieces of pottery. The choice of technique and material depends on the potter’s skills, preferences, and the desired outcome.
Types of Pottery
Pottery has a long history and has evolved over time to include various types. Some of the most common types of pottery include:
- Earthenware: Earthenware is one of the oldest and most basic types of pottery. It is made from clay that is fired at a low temperature. Earthenware often has a porous, porous, and less durable than other types of pottery. It is commonly decorated with colorful glazes and used for everyday items like dishes and vases.
- Stoneware: Stoneware is a type of pottery that is fired at a higher temperature than earthenware. This results in a harder, more durable piece that is less porous. Stoneware is commonly used for tableware, cookware, and decorative items. It can be glazed or left unglazed.
- Porcelain: Porcelain is a type of pottery that is fired at an even higher temperature than stoneware. It is known for its translucency, strength, and white color. Porcelain is often used for fine china, figurines, and decorative pieces. It is usually glazed to create a smooth and shiny finish.
- Majolica: Majolica is a type of pottery that originated in Spain and Italy in the 14th century. It is characterized by its bright and colorful glazes, often in intricate patterns. Majolica is typically made from earthenware and is used for decorative items like plates, vases, and tiles.
- Raku: Raku is a Japanese pottery technique that originated in the 16th century. It involves removing pieces from the kiln while they are still hot, often resulting in unique and unpredictable patterns and colors. Raku pottery is primarily used for tea ceremonies and decorative pieces.
These are just a few examples of the many types of pottery that exist. Each type has its own unique characteristics and uses, but they all share the common element of being created from clay and fired to transform it into a durable and functional object.
The History of Ceramics
The history of ceramics can be traced back thousands of years, making it one of the oldest forms of art and technology. The origins of ceramics can be found in ancient civilizations such as China, Egypt, and Mesopotamia.
One of the earliest known ceramics is pottery, which dates back to around 10,000 BCE. Pottery was initially used for practical purposes, such as creating storage vessels and cooking pots. It was made by shaping clay and then firing it at high temperatures to harden it.
In ancient China, ceramics played a significant role in daily life. The Chinese were known for their advanced techniques in pottery making, including the use of a pottery wheel and glazes. The Chinese also developed porcelain, a type of ceramic that is known for its delicate and translucent appearance.
In ancient Egypt, ceramics were also widely used. Egyptians made various types of pottery, including storage jars, vessels, and figurines. They were skilled in creating intricate designs and patterns on their pottery using techniques such as painting and carving.
In Mesopotamia, ceramics were essential for both practical and decorative purposes. The Mesopotamians were known for their use of kilns and advanced glazing techniques. They created a wide range of ceramics, from simple clay cups to highly detailed sculptures.
Throughout history, ceramics have continued to evolve and develop. Different cultures and civilizations have contributed to the advancement of ceramic techniques and styles. Today, ceramics are not only used for practical purposes but also have become a popular form of art and self-expression.
| Time Period | Main Developments |
|---|---|
| 10,000 BCE | Earliest pottery |
| Ancient China | Introduction of pottery wheel and porcelain |
| Ancient Egypt | Intricate designs and patterns |
| Mesopotamia | Use of kilns and advanced glazing techniques |
The history of ceramics is a testament to the creativity and skill of human beings. It provides a window into the past, allowing us to understand the cultural, technological, and artistic achievements of ancient civilizations.
Applications and Uses of Ceramics
Ceramics have been utilized for a wide range of applications due to their unique properties and characteristics. Whether in industrial or domestic settings, ceramics play a vital role in various fields. Here are some of the most common applications and uses of ceramics:
- Construction: Ceramics are extensively used in the construction industry. They are used to make tiles, bricks, cement, and other structural components. Ceramic materials offer durability, resistance to heat and chemicals, and low maintenance, making them ideal for applications such as flooring, roofing, and wall coverings.
- Electronics: Ceramics find wide applications in the electronics industry. Their excellent electrical insulating properties and thermal stability make them suitable for manufacturing components such as capacitors, resistors, semiconductors, and printed circuit boards (PCBs). Ceramics also provide mechanical strength, allowing them to withstand harsh operating conditions in electronic devices.
- Medical and Dental: Ceramics are extensively used in medical and dental applications. They are used to manufacture dental implants, prosthetics, orthopedic implants, and surgical tools. Ceramic materials offer biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and excellent wear properties that are essential for medical devices.
- Automotive: Ceramics play an important role in the automotive industry. They are used in the manufacturing of engine components, exhaust systems, brakes, and catalyst supports. Ceramics offer high temperature resistance, low thermal expansion, and excellent mechanical properties, providing durability and reliability in automotive applications.
- Aerospace: Ceramics find significant applications in the aerospace industry. They are used in the production of turbine blades, heat shields, rocket nozzles, and other high-temperature components. Ceramic materials possess excellent thermal stability, high strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion, making them suitable for extreme aerospace conditions.
In addition to these applications, ceramics are also utilized in various other fields such as energy generation, chemical processing, defense, and environmental protection. The versatility and unique properties of ceramics make them indispensable in modern technological advancements.
Differences in Production Methods
Although pottery and ceramics are often used interchangeably, they have significant differences in their production methods.
- Forming Technique: Pottery is typically created through a technique called throwing, where the ceramic material is shaped on a potter’s wheel. Ceramics, on the other hand, can be formed through various techniques, including throwing, hand-building, and molding.
- Firing Process: Pottery is typically fired at a lower temperature, usually between 1800 and 2100 degrees Fahrenheit, in a kiln. This firing process results in a more porous and less durable finished product. Ceramics, on the other hand, are fired at higher temperatures, often above 2300 degrees Fahrenheit, which makes them denser and more durable.
- Types of Clay: Pottery is made from clay that is often lower in quality and contains impurities, such as iron. It is more malleable and easier to manipulate on the potter’s wheel. Ceramics, on the other hand, can be made from a wider range of clays, including higher quality clays with fewer impurities.
- Surface Finish: Pottery is often left unglazed or finished with a simple glaze to enhance its appearance. Ceramics, on the other hand, can be finished with a wide range of glazes, resulting in a smoother and more colorful surface.
- Functionality: Pottery is often used for practical purposes, such as cooking and storing food, due to its more porous nature. Ceramics, on the other hand, are often used for decorative purposes due to their denser and more durable nature.
In conclusion, while both pottery and ceramics involve the use of clay and firing processes, they differ in their forming techniques, firing processes, types of clay used, surface finishes, and functionality. Understanding these distinctions can help in appreciating the unique qualities of each art form.
Physical Properties: Pottery vs Ceramics
Pottery
- Pottery is typically made from clay that is molded and shaped.
- It is generally porous and not completely waterproof.
- Has a lower firing temperature compared to ceramics.
- Has a lower strength and durability compared to ceramics.
- Can be glazed to enhance its appearance and make it more waterproof.
- Traditionally used for functional items such as pots, bowls, and dishes.
Ceramics
- Ceramics can be made from a variety of materials, including clay, porcelain, and stoneware.
- It is non-porous and waterproof.
- Requires a higher firing temperature to achieve its desired strength and durability.
- Offers greater strength and durability compared to pottery.
- Can be glazed or left unglazed.
- Used for a wide range of purposes, including decorative items, tiles, and industrial applications.
In summary, while both pottery and ceramics are made from clay-based materials, they have distinct physical properties. Pottery is generally porous, has a lower firing temperature, and is less durable compared to ceramics. Ceramics, on the other hand, are non-porous, require a higher firing temperature, and are known for their strength and durability.
FAQ:
What is the difference between pottery and ceramics?
Pottery is a type of ceramic, but not all ceramics are pottery. Pottery refers specifically to objects that are made from clay and then fired at high temperatures to create a hard, durable material. Ceramics, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of materials, including clay, porcelain, stoneware, and earthenware, as well as other non-clay materials. Ceramics can be fired to different temperatures and have various uses, such as in the production of tiles, sculpture, and kitchenware. So, while pottery is a type of ceramic, ceramics cover a wider spectrum of materials and applications.
Can you explain the process of making pottery?
The process of making pottery begins with gathering clay, which is often found near rivers or in specific clay pits. The clay is then prepared by removing impurities and forming it into a workable consistency. Next, the potter shapes the clay by hand or using a pottery wheel, creating the desired form. Once shaped, the pottery is left to dry before being fired in a kiln. During the firing process, the pottery is subjected to high temperatures, which causes the clay particles to fuse together, creating a hard, durable material. After firing, the pottery can be decorated and glazed to enhance its appearance and functionality.
What are some examples of ceramics that are not pottery?
There are many examples of ceramics that are not pottery. Some common examples include porcelain, which is often used in the production of fine china and decorative objects; stoneware, which is used for durable dinnerware and oven-safe cookware; and earthenware, which is a type of pottery that is fired at a lower temperature and often used for everyday items like mugs and bowls. Additionally, there are non-clay ceramics, such as glass and cement, which are used in a variety of applications. Each type of ceramic has its own unique properties and uses.
Is pottery considered a form of art?
Yes, pottery is considered a form of art. While pottery can certainly have functional purposes, it is also appreciated for its aesthetic qualities. Skilled potters can create beautifully shaped vessels, intricate patterns, and unique textures through their craft. Pottery can also be seen as a form of self-expression, as potters often incorporate their own style and personality into their work. Additionally, pottery has a long history and cultural significance, with different regions around the world having their own unique pottery traditions. So, while pottery can certainly be a functional object, it is also widely recognized and appreciated as an art form.