Pottery and ceramics are often used interchangeably, but they actually refer to different things. While both involve the shaping and firing of clay, there are subtle distinctions that set them apart. By understanding these differences, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the art forms and their unique qualities.
Pottery generally refers to objects that are made from clay and then fired at a relatively low temperature, typically around 1,000 to 1,200 degrees Celsius. The resulting object is often porous and may require a glaze to make it watertight. Pottery has a long history and is one of the oldest art forms known to mankind. It can range from functional objects like bowls and plates to decorative pieces.
Ceramics, on the other hand, encompass a broader range of materials and firing techniques. While clay is still a primary component, ceramics can also include materials like glass, porcelain, and cement. Ceramics are fired at higher temperatures, typically around 2,300 to 2,900 degrees Celsius, which results in a stronger, more durable product. This allows for a wider range of applications, from delicate porcelain figurines to rugged tiles and bricks.
Both pottery and ceramics are rich in cultural and artistic significance. The process of creating these objects requires patience, skill, and knowledge of the materials. Whether it’s the intricate details on a ceramic vase or the rustic charm of a handcrafted pottery bowl, these art forms offer us a glimpse into the history and creativity of different cultures around the world.
The Difference Between Pottery and Ceramics
Pottery and ceramics are often used interchangeably, but they actually have distinct differences. While they both involve the use of clay and the firing process, they differ in terms of their composition, functionality, and historical context.
Composition
Pottery refers to objects made from clay that is fired at a relatively low temperature, usually below 1200 degrees Celsius. It is typically porous and may require additional glazing or coating to make it impermeable to liquids. Ceramics, on the other hand, are made from a broader range of materials, including clay, but also can include materials like glass and metal. They are often fired at higher temperatures, above 1200 degrees Celsius, which results in a vitrified and non-porous surface.
Functionality
Pottery has traditionally been associated with functional objects like bowls, plates, and cups, although it can also include decorative items. Ceramics, on the other hand, have a wider range of applications and can include everything from decorative sculptures to industrial components like engine parts and electrical insulators.
Historical Context
The distinction between pottery and ceramics also has historical connotations. Pottery has a long and rich history dating back thousands of years, with cultural and archaeological significance in many civilizations. It has been used for practical purposes like cooking, storage, and artistic expression. Ceramics, on the other hand, emerged later with the advancement of technology and the discovery of new materials. It is often associated with more contemporary art forms and industrial applications.
Conclusion
In summary, while pottery and ceramics share similarities in terms of working with clay and firing processes, they have key differences in their composition, functionality, and historical context. Pottery is made from clay and fired at lower temperatures, usually for functional purposes, while ceramics are made from a wider range of materials and fired at higher temperatures, with more diverse applications. Understanding these distinctions can provide insights into the artistic, cultural, and technical aspects of these art forms.
Understanding the Distinction
In the world of art and craftsmanship, the terms “pottery” and “ceramics” are often used interchangeably. However, there is a distinct difference between these two terms that sets them apart.
Pottery
Pottery refers to objects made from clay, which is a soft and malleable material. It has been used by humans for thousands of years to create functional and decorative items. Pottery is typically handcrafted by artisans through various techniques such as handbuilding, throwing on a wheel, and molding. The production of pottery involves shaping the clay, drying it, and then firing it in a kiln at high temperatures to harden it. It may also involve applying glazes for added color and a smooth finish.
Pottery is often associated with vessels such as bowls, cups, plates, and vases, which are used for holding liquids or other substances. It is known for its practicality and functionality, making it an essential part of our daily lives.
Ceramics
Ceramics, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses not only pottery but also other materials such as porcelain, earthenware, and stoneware. While pottery is a subset of ceramics, ceramics can refer to any objects made from baked clay or other inorganic materials.
Ceramic objects can be handcrafted or machine-made and can serve both functional and decorative purposes. They can range from delicate and ornate porcelain figurines to durable and utilitarian stoneware plates. The production process for ceramics may involve multiple stages, including shaping the material, glazing, and firing in a kiln.
The Distinction
In summary, the distinction lies in the scope of the term. Pottery specifically refers to objects made from clay, while ceramics is a broader category that includes pottery and other materials. So, while all pottery can be considered ceramics, not all ceramics are necessarily pottery.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for appreciating and categorizing different types of ceramic art. Whether you’re a collector or a creator, having a clear understanding of the terminology can help you navigate the world of pottery and ceramics more effectively.
Pottery: An Overview
Pottery refers to the art and process of creating objects out of clay. It is one of the oldest and most widespread forms of art and craftsmanship, with evidence of pottery production dating back to at least 10,000 years ago. Pottery is an important part of many cultures and has been used for both practical and decorative purposes.
There are various techniques used in pottery, including hand-building, wheel throwing, and slipcasting. Hand-building involves shaping the clay by hand, using techniques such as coiling, pinching, and slab construction. Wheel throwing, on the other hand, involves shaping the clay on a pottery wheel, creating symmetrical forms. Slipcasting involves pouring liquid clay (slip) into a mold and allowing it to set before removing it.
Clay is the primary material used in pottery, and it can vary in composition and color. Different types of clay have different qualities, such as plasticity, hardness, and the ability to hold its shape. Common types of clay used in pottery include earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain.
Once the clay has been shaped, it is typically fired in a kiln to harden it and make it durable. The firing process involves heating the pottery to high temperatures, which causes the clay particles to fuse together and become rigid. After the initial firing, pottery can be further decorated with glazes, paints, or other surface treatments.
Pottery has a wide range of uses, both functional and artistic. It is commonly used for making vessels such as bowls, plates, and vases, as well as tiles, sculptures, and figurines. In addition to its practical uses, pottery is also valued for its aesthetic qualities and has been a medium for artistic expression throughout history.
| Durability | Pottery is highly durable and can last for thousands of years when properly cared for. |
| Versatility | Clay can be shaped and formed into a wide range of objects, allowing for endless possibilities in design. |
| Functionality | Many pottery objects, such as bowls and plates, are functional and can be used in everyday life. |
| Artistic Expression | Pottery allows artists to express their creativity and create unique and individual pieces. |
In conclusion, pottery is a versatile and enduring art form that has been a part of human culture for thousands of years. Its combination of practicality and artistic expression makes it a valuable and enriching medium for both artists and consumers.
Ceramics: An Overview
Ceramics is a broad term that refers to the art and science of making objects from clay or other inorganic non-metallic materials. It encompasses a wide range of techniques and styles, including pottery, sculpture, and decorative objects.
Historical Background:
Ceramic objects have been created for thousands of years, with evidence of early ceramics dating back to 24,000 BC. Throughout history, ceramics have played a significant role in various cultures and civilizations, serving both utilitarian and artistic purposes.
Types of Ceramics:
There are several different types of ceramics, each with its own characteristics and uses:
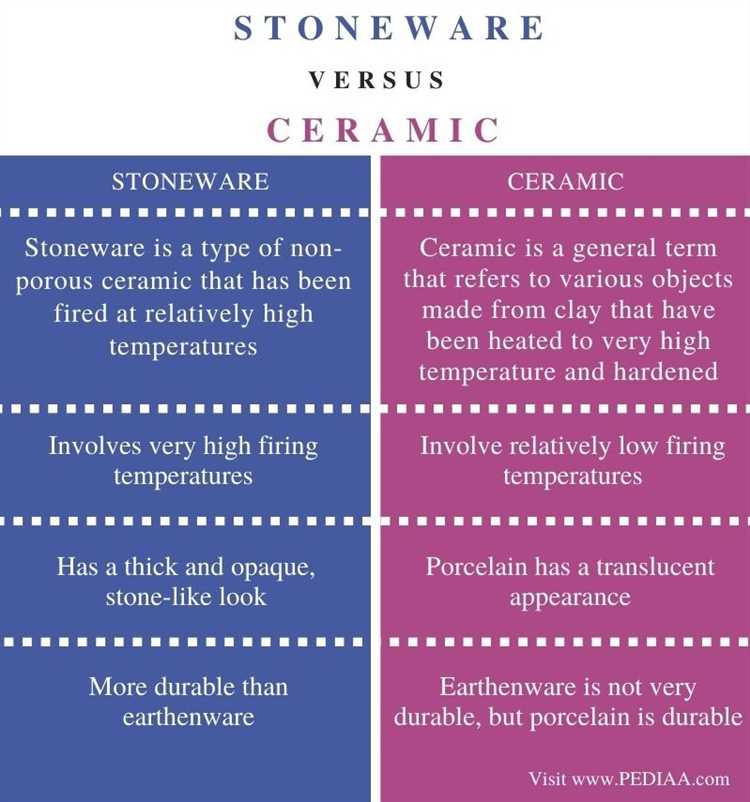
- Earthenware: This is the oldest type of ceramic and is known for its porous nature and low firing temperature. Earthenware is often used for everyday objects like dishes and tiles.
- Stoneware: Stoneware is a durable and dense ceramic that is fired at a higher temperature than earthenware. It is commonly used for kitchenware, dinnerware, and decorative pottery.
- Porcelain: Porcelain is a type of ceramic known for its delicate and translucent appearance. It is fired at a high temperature and is often used for fine china, figurines, and decorative objects.
Techniques and Processes:
The creation of ceramics involves various techniques and processes, including:
- Handbuilding: This involves forming clay by hand, using techniques like pinch pottery, coiling, and slab construction.
- Throwing: Throwing is a technique where a potter shapes clay on a potter’s wheel, allowing for precise control and symmetry.
- Molding: Molding involves creating ceramic objects using molds, which can be made of plaster or other materials.
- Firing: Firing is the process of heating ceramics in a kiln, which hardens the clay and creates a permanent object.
- Glazing: Glazing involves applying a liquid mixture of minerals and pigments to ceramics before firing, resulting in a glossy or matte surface and adding color and protection.
Applications and Significance:
Ceramics have numerous applications and are used in various industries, including art, architecture, household items, and technology. They are valued for their durability, heat resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Additionally, ceramics have played a significant role in cultural and artistic expressions throughout history and continue to be highly regarded in the contemporary art world.
In conclusion, ceramics encompass a wide range of objects and techniques, making it an essential part of human history and culture. From ancient pottery to modern sculptural works, ceramics continue to captivate and inspire with their versatility and beauty.
Historical Significance
The history of pottery and ceramics dates back thousands of years to the earliest human civilizations. Both pottery and ceramics have played significant roles in the development of human culture and society.
One of the earliest forms of pottery can be traced back to around 24,000 BC in the Paleolithic era. It is believed that pottery was used for practical purposes, such as storing food and water, and as a means of artistic expression. The invention of pottery marked a significant shift in human history as it allowed for the development of settled communities and the transition from a nomadic lifestyle to an agricultural one.
Throughout history, pottery and ceramics have been closely linked to the culture, traditions, and technology of various civilizations. For example, ancient Egyptian pottery was intricately decorated and featured symbolic designs that conveyed religious and cultural beliefs. In ancient China, ceramics were highly valued and used as status symbols by the ruling class.
The development of new techniques and technologies in pottery and ceramics has often coincided with major historical events. For instance, the invention of the potter’s wheel in Mesopotamia around 3,000 BC revolutionized the production process and allowed for the creation of more complex vessels. The invention of glazing techniques also marked a significant advancement in ceramics, as it provided a way to create vibrant colors and enhance the durability of the objects.
Over time, pottery and ceramics have also been influenced by cultural exchange and trade between different civilizations. For example, during the Islamic Golden Age, Persian ceramics greatly influenced the development of pottery in the Mediterranean region. Similarly, the Spanish colonization of the Americas introduced European ceramic techniques to indigenous civilizations, resulting in the creation of new and unique ceramic styles.
Today, pottery and ceramics continue to be valued for their historical significance and artistic value. They serve as a means of preserving cultural heritage, as well as a medium for contemporary artists to express their creativity. From functional pottery to decorative ceramics, this ancient art form continues to evolve and captivate people around the world.
Pottery in Ancient Civilizations
Pottery has been an integral part of ancient civilizations throughout history. It played a crucial role in the development of these civilizations, and its production techniques and styles were influenced by various factors, including geography, culture, and technology.
Ancient civilizations such as the Mesopotamians, Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans were known for their exceptional pottery skills. They created beautiful and intricate pottery pieces that served both utilitarian and decorative purposes.
One of the earliest known civilizations to have developed pottery techniques is the Mesopotamian civilization. They were skilled in using the potter’s wheel and produced a wide range of pottery vessels, including bowls, jars, and cups. These vessels were adorned with intricate designs and patterns, reflecting the artistic nature of the civilization.
The Egyptians also had a rich pottery tradition. They used pottery for various purposes, such as storage, cooking, and ceremonial rituals. They developed advanced pottery techniques, including the use of glazes and vibrant colors. The Egyptians were also known for their detailed and realistic pottery figurines, which were often placed in tombs as grave goods.
The ancient Greeks are renowned for their distinctive pottery styles, particularly the black and red-figure pottery. They developed sophisticated painting techniques, allowing them to create intricate and detailed scenes on their pottery vessels. These scenes often depicted mythological and everyday life events.
The Romans, influenced by both the Greeks and the Egyptians, also made significant contributions to pottery production. They developed new forms and styles, such as the terra sigillata, which was highly prized for its smooth red surface. The Romans also created pottery molds, enabling mass production of standardized vessels.
Overall, pottery in ancient civilizations served as a way to store and transport goods, as well as a form of artistic expression. It played a crucial role in defining the cultural identity of these civilizations and continues to be a valuable source of historical and artistic information.
Ceramics in Ancient Cultures
The art of ceramics has been practiced by various ancient cultures around the world for thousands of years. These early civilizations developed their own unique techniques and styles, using ceramics for both practical and artistic purposes.
China: One of the oldest known ceramic traditions can be traced back to ancient China, where pottery was first created during the Neolithic period around 10,000 BCE. Chinese ceramics are known for their exquisite craftsmanship and intricate designs. The country became famous for producing delicately painted porcelain pieces, such as vases, bowls, and figurines.
Greece: Ancient Greece also had a rich ceramic culture, and pottery played a significant role in their daily lives. Greek pottery was often decorated with intricate patterns and scenes depicting mythological figures and events. The Greeks used ceramics for storage vessels, as well as for drinking and dining purposes.
Egypt: In ancient Egypt, ceramics were highly valued and were used for both practical and religious purposes. The Egyptians developed sophisticated pottery techniques, producing vessels with a variety of shapes and sizes. Ceramics played a significant role in their burial practices, with the use of funerary jars and figurines.
Mesoamerica: The ancient civilizations of Mesoamerica, including the Mayans and Aztecs, also had a rich ceramic tradition. They used ceramics for various purposes, including cooking vessels, figurines, and ceremonial objects. These civilizations had distinct styles and techniques, with intricate decorations and symbolic imagery.
Rome: The ancient Romans were skilled ceramicists and played a vital role in the development of pottery techniques. They introduced the use of the potter’s wheel, which greatly improved efficiency in production. Roman ceramics were often painted with detailed scenes and were used for everyday items such as household wares and oil lamps.
India: Ceramic traditions in ancient India date back to the Indus Valley Civilization around 2500 BCE. The pottery of this region was known for its precision and intricate designs. Ceramics in India had both practical and artistic purposes, with the production of pottery used for cooking, storage, and religious rituals.
Ceramics in ancient cultures played a crucial role in their daily lives, as well as in their artistic and religious expressions. These early civilizations contributed to the development and advancement of ceramic techniques and styles, laying the foundation for the modern ceramic art we see today.
Production Techniques
Both pottery and ceramics are produced using various production techniques. These techniques involve shaping and decorating the clay to create the desired finished product.
Hand-building: Hand-building is a technique where the pottery or ceramics are shaped by hand, without the use of a potter’s wheel. This technique involves using basic hand tools and molds to shape the clay.
Throwing: Throwing is a technique used specifically for pottery, where the potter uses a potter’s wheel to shape the clay. The potter’s wheel allows for greater control and precision in creating symmetrical forms.
Slipcasting: Slipcasting is a technique commonly used for ceramics. It involves creating a mold of the desired shape and pouring a liquid clay mixture, called slip, into the mold. The mold absorbs the water from the slip, leaving a solid clay object when the excess slip is poured out.
Press molding: Press molding is another technique used for ceramics. It involves pressing clay into a mold using a hydraulic or mechanical press. This method allows for the mass production of identical ceramic objects.
Glazing: Glazing is a technique used in both pottery and ceramics. Glazes are liquid mixtures applied to the surface of the clay objects. When fired in a kiln, the glaze fuses with the clay, creating a smooth, durable, and often colorful surface.
Firing: Firing is the final step in the production process, where the shaped and glazed clay objects are heated in a kiln at high temperatures. This firing process hardens the clay, making it permanent and transforming it into pottery or ceramics.
In conclusion, both pottery and ceramics employ a variety of production techniques to shape and decorate clay objects. Whether it is through hand-building, throwing, slipcasting, press molding, glazing, or firing, these techniques allow artists and artisans to create unique and functional pieces of art.
Pottery Production Methods
Pottery production methods vary depending on the desired outcome and the culture in which the pottery is being made. Here are a few common methods:
- Hand-building: This method involves shaping clay by hand, without the use of a pottery wheel. Techniques such as pinch, coil, and slab building can be used to create various forms.
- Throwing on a pottery wheel: The pottery wheel is a rotating platform that allows the potter to shape clay into symmetrical forms. Using this method, potters can create vessels such as bowls, plates, and cups.
- Mold casting: In this method, a plaster mold is created and clay is pressed into the mold to take its shape. This allows for the production of multiple identical pieces.
- Slipcasting: Similar to mold casting, slipcasting involves pouring liquid clay (slip) into a plaster mold. The mold absorbs moisture from the slip, creating a layer of solid clay. The excess slip is then poured out, leaving behind the desired shape.
- Extrusion: Extrusion involves forcing clay through a shaped opening to create long, uniform shapes. This method is often used for creating handles, spouts, and other decorative elements.
Pottery can also be decorated using various techniques such as glazing, painting, or carving. These methods add color, texture, and patterns to the finished pieces, enhancing their aesthetic appeal.
Each pottery production method requires skill, experience, and an understanding of clay properties. The choice of method depends on the potter’s preference, the desired outcome, and the intended use of the pottery.
Ceramics Production Techniques
There are several production techniques used in ceramics that help create the unique and diverse range of pottery and ceramic items. These techniques involve different processes and methods to shape, decorate, and fire clay, resulting in various textures, colors, and finishes.
1. Handbuilding
Handbuilding is one of the oldest ceramic techniques, dating back thousands of years. It involves shaping clay by hand using simple tools and techniques such as pinching, coiling, and slab building. Handbuilding allows for greater artistic expression and creativity, as each piece can be individually crafted and customized.
2. Wheel Throwing
Wheel throwing is another popular ceramics technique that involves shaping clay on a potter’s wheel. It requires skill and precision to center the clay on the wheel and then shape it into various forms such as bowls, vases, and plates. This technique allows for consistent and symmetrical shapes due to the rotational movement of the wheel.
3. Slip Casting
Slip casting is a technique used to create pottery items with uniform shapes and details. It involves pouring liquid clay, called slip, into a plaster mold. The mold absorbs moisture from the slip, leaving a solid clay shape inside. After drying, the piece is removed from the mold and further finished and fired.
4. Press Molding
Press molding is a technique where clay is pressed into a mold using a press or hydraulic machine. This method allows for the quick and efficient production of multiple identical pieces. It is commonly used for creating small and medium-sized ceramic items such as tiles, ornaments, and decorative objects.
5. Decorating and Glazing
Once the pottery or ceramic item is formed, it can be decorated and glazed to enhance its appearance. Decorating techniques include carving, painting, etching, and applying various surface treatments. Glazing involves applying a layer of liquid glass-forming substance over the surface of the piece, which melts and becomes a protective and decorative coating when fired in a kiln.
6. Firing
After decorating and glazing, the pottery or ceramic piece needs to be fired in a kiln to achieve its final hardness and durability. Firing involves subjecting the piece to high temperatures, typically between 1,000 to 2,400 degrees Fahrenheit (538 to 1,316 degrees Celsius), depending on the type of clay and desired results. The firing process transforms the clay into a ceramic material, making it strong and suitable for everyday use.
These are just a few of the many ceramics production techniques that are used by artists and artisans around the world. Each technique offers a unique approach to working with clay and allows for endless creativity and expression in the world of ceramics.
FAQ:
What is the difference between pottery and ceramics?
Pottery refers to objects made of clay that are hardened by heat, while ceramics is a broader term that includes pottery but also encompasses other materials such as porcelain and stoneware.
Can you explain the process of making pottery?
Yes, the process of making pottery typically involves shaping the clay by hand or using a potter’s wheel, drying it to remove water, and then firing it in a kiln at high temperatures to harden it.
What are some examples of ceramics?
Some examples of ceramics include porcelain, stoneware, earthenware, and bone china. These materials are often used to make dishes, vases, and decorative objects.
Is pottery considered as a form of art?
Yes, pottery is often considered a form of art. It allows artists to express their creativity through the use of clay and various techniques such as sculpting, glazing, and surface decoration.
What are the main characteristics of pottery?
The main characteristics of pottery include its natural, earthy appearance, its ability to hold liquids, and its durability. Pottery is also known for its unique textures and glazes.