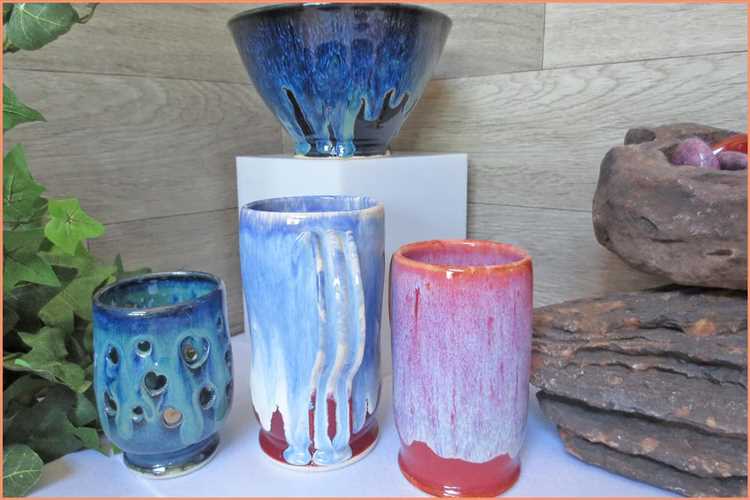
Creating pottery glaze is a intricate and fascinating art form that adds depth, color, and texture to ceramics. The process involves blending minerals, chemicals, and other materials to achieve the desired appearance and properties. Whether you are a seasoned potter or just starting out, learning how to create your own pottery glaze can be a rewarding and creative journey.
In this step-by-step guide, we will explore the basic principles of pottery glaze creation and provide you with the knowledge and techniques to get started. From understanding the different types of glaze materials to experimenting with colorants and additives, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of the art and science behind pottery glaze.
Throughout history, pottery glazes have played a crucial role in defining the aesthetics and functionality of ceramics. From ancient civilizations to contemporary artists, the art of pottery glaze has evolved and developed, resulting in a wide range of techniques and styles.
By following this step-by-step guide, you will learn how to formulate glaze recipes, test for consistency and durability, and apply glazes to your ceramic pieces. Whether you prefer rich earth tones or vibrant cobalt blues, you will have the tools and knowledge to create unique and stunning pottery glazes that reflect your artistic vision.
Choosing the Right Clay for Glazing
When it comes to pottery glazing, choosing the right clay is essential for achieving the desired results. Different clays have different characteristics that can greatly affect the outcome of your glaze application. Here are some important factors to consider when selecting clay for glazing:
- Porosity: Porosity refers to the ability of clay to absorb water. It is important to choose a clay with the right level of porosity for glazing, as this will affect how the glaze adheres to the surface of the clay and how the colors will develop.
- Firing temperature: Different clays have different firing temperatures, and it’s important to choose one that is compatible with the glaze you plan to use. Firing at the wrong temperature can result in the glaze not adhering properly or even melting off the piece.
- Texture: The texture of the clay can also impact the final appearance of the glazed piece. Some clays have a smoother texture, while others have a more coarse or grainy texture. Consider the desired look and feel of your finished piece when selecting clay for glazing.
- Color: While clay is often thought of as being natural or earth-toned, there are also clays available in a wide range of colors. Consider the color of the clay when selecting one for glazing, as it can affect how the glazes interact with the clay and how the final colors appear.
- Availability: Finally, consider the availability of the clay you are considering. Some clays may be more difficult to find or more expensive than others. It’s important to choose a clay that is easily accessible and fits within your budget.
| Clay Type | Porosity | Firing Temperature | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earthenware | High | Low to medium | Smooth |
| Stoneware | Medium to low | Medium to high | Smooth to coarse |
| Porcelain | Low | High | Smooth |
These are just a few examples of clay types commonly used for glazing. It’s important to do your research and experiment with different clays to find the one that best suits your glazing needs and artistic vision.
Remember, selecting the right clay for glazing is essential for achieving the desired results. Consider factors such as porosity, firing temperature, texture, color, and availability when choosing your clay. With the right clay, you’ll be on your way to creating beautiful glazed pottery.
Understanding the Basics of Glaze Chemistry
The art of creating pottery glaze involves understanding the fundamentals of glaze chemistry. Glazes are essentially a combination of minerals and chemicals that undergo chemical reactions during the firing process to form a glassy coating on the surface of the pottery.
Composition:
Glazes are typically composed of three main components:
- Flux: Fluxes are responsible for reducing the melting point of the glaze mixture. Common fluxes used in pottery glazes include feldspars, borax, and lithium carbonate. The choice of flux affects the final appearance and functionality of the glaze.
- Stabilizer: Stabilizers help to control the expansion and contraction of the glaze during the firing process. Alumina and silica are common stabilizers used in pottery glazes.
- Colorants: Colorants are added to the glaze mixture to achieve different colors. Metal oxides, such as iron oxide for brown or copper oxide for green, are commonly used as colorants.
Oxidation and Reduction:
The atmosphere in the kiln during firing plays a crucial role in glaze chemistry. Oxidation firing involves a sufficient supply of oxygen in the kiln, while reduction firing limits the oxygen supply. The choice of firing atmosphere affects the final color and surface of the glaze.
Melting Temperature:
The melting temperature of a glaze, also known as the maturing temperature, determines when the glaze will properly fuse and form a glassy surface. The maturing temperature is influenced by the composition of the glaze, particularly the flux used.
Testing and Adjusting:
Creating the perfect glaze requires a process of trial and error. Glaze recipes can be adjusted by changing the ratios of fluxes, stabilizers, and colorants to achieve desired results. It is important to test glazes on small test tiles before applying them to larger pottery pieces.
| Ingredient | Common Source |
|---|---|
| Feldspar | Mineral deposits |
| Borax | Naturally occurring mineral |
| Lithium carbonate | Chemical compound |
| Alumina | Clay minerals |
| Silica | Quartz or flint |
| Iron oxide | Naturally occurring mineral |
| Copper oxide | Naturally occurring mineral |
Understanding the basics of glaze chemistry is essential for any potter looking to create unique and beautiful pottery pieces. By experimenting with different glaze compositions and firing atmospheres, potters can achieve fascinating results and truly explore the art of creating pottery glazes.
Preparing Your Workspace and Tools
Before you begin creating pottery glaze, it is essential to prepare your workspace and gather all the necessary tools. This will ensure that you have a clean and organized area to work in and that you have everything you need to create the glaze properly.
1. Clear and Clean the Workspace
Clear an area in your studio or workspace where you can comfortably work on creating the pottery glaze. Make sure the area is clean and free from any dust or debris that can contaminate the glaze.
2. Gather the Necessary Tools
Collect all the tools and materials you will need to create the pottery glaze. Some of the essential tools include:
- Measuring tools such as measuring cups and spoons
- A scale to weigh the ingredients
- A mixing container
- A stirring stick or whisk
- A sieve or strainer
3. Organize Your Ingredients
Make sure you have all the ingredients required for the pottery glaze recipe. Organize them in separate containers or bowls to have them ready for use. It is also helpful to label each container with the ingredient name.
4. Set Up a Ventilation System
Pottery glaze recipes often involve mixing dry ingredients, which can create dust particles that may be harmful if inhaled. Ensure there is adequate ventilation in your workspace by opening windows or using a ventilation fan or hood to remove any fumes or particles.
5. Prepare Safety Measures
Working with pottery glaze can involve potential hazards, so it is essential to take safety measures. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby, wear protective gloves and goggles, and follow proper safety guidelines while handling and mixing the ingredients.
6. Arrange Your Workspace
Organize your workspace in a way that makes it easy for you to access your tools and ingredients. Arrange your materials in a logical order and have enough space to work comfortably.
7. Clean and Maintain Tools
Before starting, make sure all your tools are clean and in good condition. Clean any mixing containers, measuring tools, and stirring sticks from previous use. This will help to prevent any contamination or unwanted reactions in the glaze.
By taking the time to prepare your workspace and gather your tools properly, you will be ready to start creating your pottery glaze with ease and efficiency.
Creating Your Own Glaze Recipe
Creating your own glaze recipe can be a fun and rewarding process. It allows you to have complete control over the colors, textures, and effects that you want to achieve on your pottery. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Research and Gather Information: Before you begin creating your own glaze recipe, it’s important to do some research and gather information about different types of glazes, their ingredients, and the effects they produce. This will give you a good foundation to start experimenting with.
- Choose Your Base: Start by choosing a base for your glaze recipe. A base glaze provides a stable foundation and holds the ingredients together. It usually consists of a combination of feldspar, kaolin, silica, and other materials that melt together when fired.
- Add Colorants: Decide on the colors you want to incorporate into your glaze and select the appropriate colorants. Colorants are usually metallic oxides or stains that are added to the base glaze to create different colors. Experiment with different combinations and proportions to achieve the desired hues.
- Add Opacifiers or Transparency Agents: Depending on the desired effect, you may want to add opacifiers or transparency agents to your glaze recipe. Opacifiers such as tin oxide or zirconium silicate give the glaze an opaque appearance, while transparency agents like alumina or magnesium carbonate increase the transparency of the glaze.
- Experiment and Test: Once you have your base glaze, colorants, and any additional ingredients, it’s time to start experimenting. Mix different proportions of each ingredient and test them on small tiles or test pieces of pottery. Take notes on the results and make adjustments as needed.
- Document Your Recipe: As you refine your glaze recipe and achieve the desired results, it’s important to document the exact proportions of each ingredient. This will allow you to recreate the glaze in the future and make any necessary adjustments.
- Firing and Finalizing: After you have finalized your glaze recipe, apply it to your pottery and fire it according to the appropriate temperature and firing schedule. Keep in mind that glazes may behave differently at different firing temperatures, so it may require some experimentation to achieve the desired result.
Creating your own glaze recipe is a creative and iterative process. Don’t be afraid to experiment and make adjustments along the way. With time and practice, you’ll be able to develop unique and beautiful glazes that are truly your own.
Mixing and Testing Your Glaze
Mixing and testing your glaze is an important step in the pottery making process. It allows you to adjust the consistency and color of your glaze to achieve the desired results. Follow these steps to ensure a successful glaze mixture and test:
- Gather your materials: Before you start mixing your glaze, make sure you have all the necessary materials on hand. This includes your glaze ingredients, a scale or measuring cups, a mixing container, and a mixing tool such as a whisk or spatula.
- Measure your ingredients: Use a scale or measuring cups to accurately measure the ingredients for your glaze. Follow the recipe or formula provided, making sure to measure both the dry and liquid ingredients carefully. The ratio of ingredients is crucial for the glaze to work properly.
- Mix the dry ingredients: Start by combining all the dry ingredients in a mixing container. Use your mixing tool to thoroughly blend the ingredients together. This will ensure an even distribution of the glaze materials.
- Add the liquid ingredients: Slowly pour the liquid ingredients into the dry mixture while continuously stirring. This will prevent clumping and ensure a smooth glaze consistency. Keep stirring until all the ingredients are well combined.
- Test the glaze: Once your glaze mixture is ready, it’s important to test it before using it on your pottery. Take a small amount of the glaze and apply it to a test tile or a sample piece of clay. Fire the test piece according to the recommended firing temperature and time for your glaze.
- Observe the results: Examine the fired test piece to see the effects of the glaze. Pay attention to its color, texture, and any other desired characteristics. If you’re satisfied with the results, your glaze is ready to use on your pottery. If not, make adjustments to the glaze recipe and repeat the testing process until you achieve the desired results.
Remember, mixing and testing your glaze is a crucial step in the pottery making process. It allows you to fine-tune your glaze to achieve the desired effects on your pottery. Take your time, experiment, and don’t be afraid to make adjustments until you find the perfect glaze for your creations.
Applying Glaze to Your Pottery
Once you have created and dried your pottery, it is time to apply the glaze. Glaze not only adds color to your pottery, but it also provides a protective coating that allows the piece to be functional and waterproof.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to apply glaze to your pottery:
- Clean the pottery: Make sure your pottery is clean and free from any dust or dirt. Use a soft cloth or sponge to wipe off any debris.
- Choose your glaze: Select the glaze you want to use based on the desired color and texture. Glazes come in a variety of colors and finishes, such as matte, glossy, or metallic.
- Stir the glaze: Before applying the glaze, give it a good stir to ensure that the color and consistency are even.
- Apply the glaze: There are several techniques for applying glaze, including dipping, brushing, and spraying. Choose the method that works best for your piece. If you are brushing the glaze, use a soft and wide brush for an even application.
- Allow the glaze to dry: After applying the glaze, let it dry completely. Follow the instructions on the glaze package for the recommended drying time.
- Fire the pottery: Once the glaze is dry, it is ready for firing. Place it in a kiln and follow the firing schedule specific to the type of glaze you used.
- Inspect the finished piece: After firing, examine your pottery to ensure that the glaze has fused properly and has the desired appearance. If there are any flaws, you can try reapplying glaze and refiring.
Remember, each glaze has its own unique characteristics, so it’s essential to experiment and test different glazes to achieve the desired results. Have fun and enjoy the process of applying glaze to your pottery!
Firing and Finishing Your Glazed Pottery
Once you have applied the glaze to your pottery, the next step is to fire it in a kiln. Firing the pottery not only helps to harden the clay but also melts the glaze and fuses it to the surface, creating a durable and beautiful finish.
Before firing your glazed pottery, it is important to make sure that it is completely dry. Any remaining moisture can cause the pottery to crack or explode during firing. You can let your pottery air dry for a few days or use a kiln to speed up the drying process.
The firing process involves heating the pottery slowly to a high temperature, typically between 1200°C and 1300°C, depending on the type of clay and glaze used. This temperature allows the glaze to melt and create a smooth, glossy surface. It is important to follow the specific firing instructions provided by the manufacturer of your clay and glaze to ensure the best results.
When loading your pottery into the kiln, make sure to leave enough space between the pieces to allow for proper airflow and heat distribution. This will help to ensure that the glaze fires evenly and avoids any unwanted reactions between pieces. You can use kiln furniture, such as stilts or shelves, to stack and support your pottery during firing.
During the firing process, it is important to monitor the temperature and make any necessary adjustments to ensure even heating. This can be done using a pyrometer or kiln controller. It is also important to keep the kiln vented to release any gases or fumes that may be produced during firing.
Once the firing process is complete, it is important to let the kiln cool down slowly to avoid any thermal shock to the pottery. Rapid temperature changes can cause the pottery to crack or break. This cooling process can take several hours or even days, depending on the size of the kiln and the thickness of the pottery.
After the kiln has cooled, you can carefully remove your glazed pottery. It is important to handle the pottery with care, as glazed surfaces can be delicate and easily scratched or damaged. You can use a soft cloth or sponge to clean any residue or dust from the surface of the pottery.
Once your glazed pottery is completely finished, you can display it proudly or use it for its intended purpose. Glazed pottery can be a beautiful and functional art form that adds a touch of elegance to any home or space.
FAQ:
What is pottery glaze?
Pottery glaze is a liquid or powdered substance that is applied to ceramics and fired in a kiln, creating a hard, glossy, and decorative coating.
What are the ingredients for making pottery glaze?
The ingredients for making pottery glaze vary depending on the desired effect, but common ingredients include silica, alumina, fluxes, colorants, and stabilizers.
How do you mix pottery glaze?
To mix pottery glaze, you first need to weigh out the dry ingredients and combine them in a bucket. Then, slowly add water and mix until the glaze reaches the desired consistency. It is important to mix the glaze thoroughly to ensure an even distribution of particles.
What is the firing temperature for pottery glaze?
The firing temperature for pottery glaze depends on the specific glaze recipe and the type of clay being used. Generally, glazes are fired at temperatures between 1,200 and 2,400 degrees Fahrenheit.
Can you make your own pottery glaze?
Yes, you can make your own pottery glaze. There are many recipes available, and it allows for greater creativity and customization in your ceramic work.
How long does it take to apply pottery glaze?
The time it takes to apply pottery glaze varies depending on the size and complexity of the piece. It can range from a few minutes to several hours, as multiple coats may be required for a desired effect.
What are some techniques for applying pottery glaze?
There are various techniques for applying pottery glaze, including dipping, pouring, brushing, spraying, and sponging. Each technique produces a different result, so it’s important to experiment and find the technique that works best for your desired outcome.