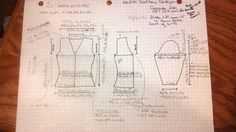
Knitting is not only a relaxing and rewarding hobby, but it can also be a great way to express your individual style and creativity. If you have been knitting for a while and have mastered the basic techniques, you may be ready to take your skills to the next level and start creating your own knitting patterns. Writing a knitting pattern may seem like a daunting task, but with the right tips and techniques, you can easily turn your ideas into a step-by-step guide that others can follow.
When it comes to writing a knitting pattern, it’s important to start with a clear plan. Before you pick up your needles and start knitting, take some time to brainstorm your design and think about the details you want to include. Consider the size and shape of your finished project, the type of yarn and needles you’ll use, and any special stitches or techniques that will be required. Having a well-thought-out plan will make it easier to write your pattern and help you avoid any confusion or mistakes along the way.
As you begin writing your knitting pattern, remember to be clear and concise in your instructions. Use simple and straightforward language, avoiding any unnecessary jargon or technical terms. This will make it easier for beginners to follow along and ensure that your pattern is accessible to knitters of all skill levels. Consider including helpful tips and explanations throughout your pattern to guide knitters through any tricky steps and provide additional support.
In addition to clear instructions, it’s also important to include accurate and detailed measurements in your knitting pattern. This will help ensure that the finished project turns out the way you intended and fits properly. Take the time to measure your gauge and include it in your pattern, as well as the finished measurements of your project. This will allow knitters to adjust their tension and choose the appropriate size for their intended recipient.
Writing a knitting pattern can be a fun and satisfying way to share your love of knitting with others. Whether you’re creating a simple scarf or a complex sweater, following these tips and techniques will help you write a clear and well-structured pattern that others can enjoy. Remember to stay organized, be clear in your instructions, and include all the necessary details. With practice and patience, you’ll soon be able to create your own knitting patterns that are both beautiful and easy to follow.
Understanding Knitting Patterns
Knitting patterns are a set of instructions that guide you through the process of creating a particular knitted item, such as a sweater, hat, or scarf. They provide step-by-step directions on how to work each stitch, row, and section of the project.
When reading a knitting pattern, it is important to understand the abbreviations and symbols used. These abbreviations represent different types of stitches, techniques, and instructions that are commonly used in knitting patterns. Some common abbreviations include:
- K: Knit
- P: Purl
- YO: Yarn over
- SSK: Slip, slip, knit
- K2tog: Knit two stitches together
Reading a knitting pattern also involves understanding the stitch and row gauge. The gauge is the number of stitches and rows per inch that you should achieve in order to match the size and fit of the finished item. It is important to knit a gauge swatch before starting the project to ensure that you are using the correct needle size and yarn weight to achieve the correct gauge.
Knitting patterns often include a list of materials needed, such as the specific yarn and needle sizes required. They may also provide measurements for different sizes, stitch counts, and any additional supplies or techniques that are needed to complete the project.
It is helpful to read through the entire knitting pattern before starting to get an understanding of the overall structure and construction of the item. This can help you anticipate any tricky techniques or stitch patterns that you may encounter along the way.
When following a knitting pattern, it is important to keep track of your progress. Many patterns include a chart or table to help you keep track of stitch counts, pattern repeats, and shaping instructions. This can be especially useful for complex patterns or those that require a lot of counting and attention to detail.
| Size | Stitch Count | Row Count |
|---|---|---|
| Small | 80 | 100 |
| Medium | 90 | 110 |
| Large | 100 | 120 |
Overall, understanding knitting patterns is essential for successfully completing a knitted project. By familiarizing yourself with the abbreviations, symbols, and instructions, you can confidently tackle any knitting pattern and create beautiful hand-knit items.
Choosing the Right Yarn and Needles
One of the most important considerations when designing a knitting pattern is choosing the right yarn and needles. The yarn and needle size you choose can greatly impact the final look and feel of the finished project.
When selecting yarn, consider the fiber content, weight, and texture. Different fibers have different properties, such as warmth, softness, and durability. The weight of the yarn, indicated by a number from 0 to 7, determines how thick or thin the yarn is. The texture of the yarn can range from smooth and silky to fluffy and textured. Choose a yarn that suits your desired project and the desired qualities of the final item.
Needles are another important consideration. The size of the needles you use will affect the tension and gauge of your knitting. The tension refers to the tightness or looseness of your stitches, while the gauge is the number of stitches and rows per inch in your knitting. It is recommended to use the needle size recommended on the yarn label, but you may need to adjust the needle size to achieve the desired tension and gauge.
There are different types of knitting needles to choose from, including straight needles, circular needles, and double-pointed needles. Straight needles are the traditional choice and are ideal for flat projects such as scarves and blankets. Circular needles have a flexible cable connecting two needle tips and are perfect for knitting in the round, such as hats and sweaters. Double-pointed needles are used for knitting small, tubular projects like socks and gloves.
It’s also worth considering the length of the needles. Longer needles are great for holding more stitches, while shorter needles are easier to handle for smaller projects. Choose the length that feels comfortable for you.
| Yarn Weight | Needle Size (US) |
|---|---|
| Fingering/Sock | 1-3 |
| Sport/DK | 3-5 |
| Worsted/Aran | 7-9 |
| Bulky/Chunky | 10-11 |
| Super Bulky/Jumbo | 13+ |
It’s important to note that these recommended needle sizes can vary depending on your personal knitting style and desired tension. Always make a gauge swatch before starting your project to ensure the needle size produces the desired results.
By carefully considering the yarn and needle choices for your knitting pattern, you can create a project that not only looks beautiful but also feels amazing to wear or use.
Basic Knitting Stitches
When it comes to knitting, there are a few basic stitches that every beginner should learn. These stitches form the foundation of almost any knitting project, and once you have mastered them, you will be able to tackle more complex patterns with confidence.
1. Knit Stitch
The knit stitch is the most basic stitch in knitting. It is commonly abbreviated as K in knitting patterns. To knit, insert the right-hand needle into the first stitch on the left-hand needle from left to right. Wrap the yarn around the right-hand needle counterclockwise, then pull the yarn through the stitch, slipping it off the left-hand needle. Practice this stitch until it becomes second nature.
2. Purl Stitch
The purl stitch is another fundamental stitch in knitting. It is commonly abbreviated as P in knitting patterns. The purl stitch creates a fabric with a raised, bumpy texture. To purl, insert the right-hand needle into the first stitch on the left-hand needle from right to left. Wrap the yarn counterclockwise around the right-hand needle, then pull the yarn through the stitch, slipping it off the left-hand needle. Practice this stitch until you are comfortable with it.
3. Garter Stitch
The garter stitch is created by knitting every row. This results in a fabric with ridges that run horizontally. To achieve the garter stitch pattern, simply knit every stitch on every row. The garter stitch is commonly used for simple scarves, blankets, and dishcloths.
4. Stockinette Stitch
The stockinette stitch is created by alternating knit and purl rows. This stitch creates a smooth, flat fabric with a distinct right side (knit side) and wrong side (purl side). To achieve the stockinette stitch, knit one row, then purl the next row. Repeat these two rows to create the pattern. The stockinette stitch is commonly used for sweaters, hats, and other garments.
5. Ribbing
Ribbing is a textured pattern created by alternating knit and purl stitches in a regular sequence. Ribbing is commonly used for cuffs, collars, and waistbands as it provides elasticity to the fabric. A common ribbing pattern is “K1, P1” which means to knit one stitch, then purl one stitch, and repeat this pattern across the row.
6. Seed Stitch
The seed stitch is a texture pattern created by alternating knit and purl stitches within the same row. The seed stitch creates a bumpy, textured fabric. To achieve the seed stitch, alternate between knitting and purling stitches within the row. For example, “K1, P1” for the first row, then “P1, K1” for the next row, and repeat these two rows to create the seed stitch pattern.
Remember, practice makes perfect when it comes to knitting stitches. Take your time and don’t be afraid to make mistakes. With a little patience and persistence, you will become comfortable with these basic stitches and be ready to take on more advanced knitting patterns.
Reading and Interpreting Knitting Charts
Knitting charts are visual representations of knitting patterns, using symbols to represent different stitches and actions. They are an alternate method of presenting knitting instructions, and many knitters find them to be a helpful tool for following complex patterns.
Understanding the Symbols:
A key component of reading knitting charts is understanding the symbols used to represent different stitches and actions. Each symbol in a chart represents a specific knitting instruction, such as knit, purl, yarn over, decrease, or stitch pattern repeat.
Commonly used symbols in knitting charts include:
- A dot (.) or blank square: Represents a knit stitch on the right side of the fabric and a purl stitch on the wrong side.
- An “x” symbol: Represents a purl stitch on the right side of the fabric and a knit stitch on the wrong side.
- A diagonal line (“/”): Represents a knit two together (decrease) on the right side of the fabric and a purl two together (decrease) on the wrong side.
- A backward diagonal line (“\”): Represents a slip slip knit (decrease) on the right side of the fabric and a slip slip purl (decrease) on the wrong side.
- An “o” or “yarn over” symbol: Represents a yarn over, which creates an extra stitch and an eyelet hole in the fabric.
Reading the Chart:
When reading a knitting chart, it is important to remember that it typically represents only one side of the fabric. The right side of the fabric is usually shown on the right side of the chart, and the wrong side is shown on the left side of the chart.
Begin by reading the chart from right to left on the right side rows and from left to right on the wrong side rows. Follow the symbols and instructions as indicated in the chart, working the corresponding stitches or actions on the appropriate rows.
Note: Some charts may indicate additional instructions or pattern repeats within brackets or parentheses, so be sure to read the accompanying written instructions carefully alongside the chart.
Interpreting Pattern Repeats:
Pattern repeats are often used in knitting charts to create stitch patterns that repeat across the row or in a specific section of the fabric. These repeats are typically indicated by brackets or parentheses with a number inside to represent the number of stitches or rows included in the repeat.
When interpreting pattern repeats, work the stitches or actions indicated within the repeat bracket the designated number of times. Once you reach the end of the repeat, return to the beginning of the bracket and work it again until the required number of repeats is completed.
Using a Legend:
Knitting charts often come with a legend or key that explains the symbols used in the chart. This legend can be referenced as needed to ensure you are interpreting the symbols correctly. Familiarize yourself with the symbols in the legend before starting to work from the chart.
Practice and Patience:
Reading and interpreting knitting charts may require some practice and patience, especially when dealing with complex patterns. Take your time and refer back to the chart and any accompanying written instructions as needed. With practice, you will become more comfortable and confident in reading and following knitting charts.
Designing Your Own Knitting Pattern
Designing your own knitting pattern can be a rewarding and creative process. Whether you have an idea for a unique garment or want to put your own twist on an existing pattern, creating your own design allows you to express your individuality and showcase your knitting skills. Here are some tips and techniques to help you get started on designing your own knitting pattern:
- Choose your project: Decide what type of item you want to create, such as a sweater, scarf, or hat. Consider your skill level and the techniques you are comfortable with.
- Gather inspiration: Look for inspiration from sources such as fashion magazines, nature, or other knitters’ patterns. Take note of interesting stitch patterns, color combinations, and construction techniques that catch your eye.
- Sketch your design: Use pencil and paper or a digital sketching tool to draw out your design. Include details such as stitch patterns, shaping elements, and dimensions.
- Choose your yarn: Select a yarn that suits the project you have in mind. Consider factors such as fiber content, weight, and color to achieve the desired look and feel of your design.
- Create a swatch: Knit a swatch using the chosen yarn and stitch pattern to determine the gauge. This will help you calculate the number of stitches and rows needed for your design.
- Write the pattern: Start by writing an outline of the steps involved in creating your design. Break down the pattern into sections, such as cast on, body, sleeves, and finishing. Use clear and concise language, and include any special instructions or stitch patterns.
- Test your pattern: Knit your design using your own pattern to ensure its accuracy and clarity. Make any necessary adjustments and revisions as you go.
- Share your pattern: Once you are satisfied with your design and pattern, consider sharing it with the knitting community. You can publish it on knitting websites, submit it to knitting magazines, or share it on social media platforms.
Designing your own knitting pattern is a creative and fulfilling endeavor that allows you to showcase your skills and create unique, one-of-a-kind pieces. By following these tips and techniques, you can bring your knitting ideas to life and share your designs with others.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
When writing a knitting pattern, it’s common to encounter some problems along the way. Here are some common issues and how to troubleshoot them:
-
Confusing or unclear instructions: One of the most common problems is when the instructions are confusing or unclear. To avoid this, make sure to double-check your instructions and consider having someone else test-knit the pattern to catch any potential issues.
-
Inconsistent gauge: Inconsistent gauge can lead to a finished project that doesn’t fit as intended. To troubleshoot this problem, always include a gauge swatch in your pattern and provide detailed instructions on how to measure and adjust gauge if necessary.
-
Mistakes in stitch counts: Mistakes in stitch counts can throw off the entire pattern. To prevent this issue, double-check your stitch counts at the end of each row or round and compare them to the stitch counts provided in the pattern instructions.
-
Missing or incorrect abbreviations: Missing or incorrect abbreviations can be confusing for knitters. To avoid this problem, make sure to include a list of all abbreviations used in the pattern and provide clear definitions for each one.
-
Unclear or confusing charts: Charts can be a great visual aid in knitting patterns, but they can also be confusing if not properly constructed. Make sure to create clear and easy-to-read charts, with consistent symbols and clear instructions on how to read them.
-
Yarn substitutions: Sometimes knitters may want to use a different yarn than the one specified in the pattern. It’s important to provide guidance on yarn substitutions, including information on yarn weight, fiber content, and yardage to help knitters make appropriate choices.
By being aware of these common problems and taking steps to prevent them, you can ensure that your knitting pattern is clear, accurate, and enjoyable for knitters to follow.
Tips and Techniques for Writing a Knitting Pattern
Writing a knitting pattern can seem like a daunting task, but with the right tips and techniques, you can create a clear and detailed pattern that knitters will love to follow. Here are some tips to help you get started:
- Start with an outline: Before you begin writing your pattern, create an outline to organize the different sections. This will help you stay organized and ensure that you include all the necessary information.
- Use clear and concise language: When writing your pattern instructions, use clear and concise language to ensure that knitters can easily understand the steps. Avoid using overly technical terms and provide explanations or definitions when necessary.
- Include a materials list: Make sure to include a detailed list of all the materials required for the project. This should include the type and amount of yarn needed, as well as the size and type of needles.
- Add stitch counts and measurements: To help knitters track their progress and ensure that their work is on track, include stitch counts and measurements at key points in the pattern. This will provide a reference point and help knitters check their gauge.
- Provide clear abbreviations and symbols: If you use any abbreviations or symbols in your pattern, make sure to provide a key or legend explaining what each one means. This will help knitters understand the instructions and avoid any confusion.
- Include helpful tips and techniques: Consider including helpful tips and techniques throughout your pattern to guide knitters and provide them with additional support. This could include suggestions for yarn substitutions, alternative stitch patterns, or tips for achieving a professional finish.
By following these tips and techniques, you can create a knitting pattern that is easy to follow and inspires knitters to create beautiful projects. Remember to test your pattern and make any necessary revisions before publishing it to ensure that it is accurate and error-free.
FAQ:
What is a knitting pattern?
A knitting pattern is a set of instructions that guides knitters on how to create a specific knitted item.
What are the essential elements of a knitting pattern?
The essential elements of a knitting pattern include the materials needed, gauge information, stitch instructions, and finishing techniques.
How do I create my own knitting pattern?
To create your own knitting pattern, you need to first determine the desired size and gauge, then choose a stitch pattern and create a swatch to test it. From there, you can write out the stitch instructions and any additional details such as shaping and finishing techniques.
What are some tips for writing a clear and easy-to-follow knitting pattern?
Some tips for writing a clear and easy-to-follow knitting pattern include using standard abbreviations, providing detailed and explicit instructions, including charts or diagrams when necessary, and organizing the information in a logical way.
How do I calculate the number of stitches needed for a knitting project?
To calculate the number of stitches needed for a knitting project, you need to determine the desired finished measurement, the gauge, and the stitch pattern. By multiplying the stitch gauge by the desired width, you can find the approximate number of stitches needed.
What should I do if I encounter a mistake in a knitting pattern?
If you encounter a mistake in a knitting pattern, it is recommended to contact the pattern designer or publisher to inform them of the error. They may be able to provide a correction or clarification. Alternatively, you can try to figure out the correct instructions by examining the pattern and using your knitting knowledge.
Are there any online resources or software available to help with writing knitting patterns?
Yes, there are several online resources and software available to help with writing knitting patterns. Some popular options include software programs specifically designed for creating knitting patterns, online knitting pattern generators, and websites that provide pattern templates and formatting guidelines.