Knitting is a popular craft that allows you to create beautiful and unique items using just a pair of needles and some yarn. But before you can start knitting, you need to have a pattern to follow. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll walk you through the steps of creating your own knit pattern, whether it’s for a sweater, a scarf, or any other project you have in mind.
The first step in making a knit pattern is choosing the right yarn and needles for your project. The type and weight of the yarn will determine the size and feel of your finished item, so it’s important to choose wisely. You’ll also need to select the appropriate needle size based on the yarn thickness and the desired tension of your knit. It’s a good idea to make a test swatch to ensure that your chosen yarn and needles result in the desired gauge.
Once you have your materials sorted, you can move on to designing your pattern. It’s helpful to start with a basic sketch of your desired item. This will give you a visual idea of how the pattern should look and help you plan out the different sections and stitches involved. You can then begin to write out the pattern instructions, taking note of the stitch patterns, increases, decreases, and any other elements that will create the desired shape and texture.
In addition to the written instructions, it’s also helpful to include charts or diagrams for more complex stitch patterns or colorwork. These visual aids can make it easier to follow along and ensure that your pattern is clear and easy to understand.
Once your pattern is complete, it’s a good idea to have someone else test it out to make sure it’s accurate and easy to follow. This can help you catch any errors or confusing instructions before you share your pattern with others. You can also consider knitting up a sample of the pattern yourself to see how it turns out and make any necessary adjustments.
Creating your own knit pattern can be a rewarding and creative process. With a little practice and experimentation, you’ll soon be able to design your own unique patterns and bring your knitting ideas to life.
How to Make a Knit Pattern: Beginner’s Guide and Tips
Knitting is a popular craft that allows you to create beautiful and functional items using just a few basic techniques. One of the first steps in knitting is creating a knit pattern, which serves as a roadmap for your project. In this beginner’s guide, we will outline the steps to help you create your own knit pattern.
Choose a Project
Before you can create a knit pattern, you need to decide what you want to make. Whether it’s a scarf, a hat, or a sweater, choosing a project will determine the overall size and shape of your pattern.
Gather Materials
Once you have chosen a project, gather all the necessary materials. This includes the appropriate yarn and knitting needles. Make sure to check the recommended gauge on the yarn label to ensure the correct needle size.
Create a Swatch
To determine the correct gauge and stitch pattern for your project, it is important to create a swatch. Follow the instructions on the yarn label or the pattern you are using. Knit a small section of fabric, and then measure how many stitches and rows per inch you have achieved.
Measurements and Calculations
Next, you will need to take measurements and calculate how many stitches and rows you will need for your desired size. For example, if you are making a scarf and want it to be 60 inches long and 8 inches wide, you will need to calculate how many stitches and rows are needed to achieve these dimensions, based on your gauge.
Create a Chart or Written Instructions
Once you have determined the stitch and row counts, you can create a chart or write out the pattern instructions. A chart is often used for complex stitch patterns, where each square represents a stitch or row. Written instructions are more common for simpler patterns.
Add Details and Finishing Touches
Finally, add any additional details or finishing touches to your knit pattern. This could include stitch variations, color changes, or shaping instructions. Make sure to include any necessary abbreviations or explanations of special techniques.
Test and Refine
Once you have created your knit pattern, it’s time to test it out. Start knitting your project following the pattern instructions and make any necessary adjustments along the way. This may involve tweaking stitch counts or making changes to the shaping.
Share and Enjoy
After refining your pattern, you can share it with others or use it to knit more items of the same design. Remember to enjoy the process and have fun experimenting with different stitch patterns and designs.
In conclusion, creating a knit pattern is an essential step in knitting. By following these beginner’s guide and tips, you will be able to make your own knit patterns and bring your knitting projects to life!
Choosing the Right Yarn and Needles
When it comes to knitting, choosing the right yarn and needles is crucial for the success of your project. Here are some tips to help you make the best choices:
- Consider the Pattern: The pattern you’re working with will often specify the recommended yarn weight and needle size. It’s important to follow these guidelines to ensure that your project turns out as intended.
- Yarn Weight: Yarn is categorized by weight, ranging from lace weight (super fine) to super bulky. The weight of the yarn will affect the drape, thickness, and overall look of your project. Consider the end use of your project and choose a yarn weight accordingly.
- Fiber Content: Yarns can be made from a variety of fibers, including wool, cotton, acrylic, and blends. Each fiber has its own unique characteristics, so consider factors such as warmth, softness, and care instructions when choosing a yarn.
- Needle Size: The needle size you choose will also affect the look and feel of your project. Smaller needles create tighter stitches, while larger needles create looser stitches. The recommended needle size will be listed in the pattern, but you can always adjust it to achieve the desired gauge.
- Consider Your Skill Level: Beginners may find it easier to work with thicker yarn and larger needles, as the stitches will be more visible and mistakes easier to identify. As you gain experience, you can experiment with different yarn weights and needle sizes to create a wider variety of projects.
- Personal Preference: Ultimately, the choice of yarn and needles will come down to personal preference. Some knitters prefer natural fibers, while others prefer synthetic fibers. It’s important to choose materials that you enjoy working with and that suit your desired project.
Keep in mind that knitting is all about experimentation and finding what works best for you. Don’t be afraid to try different yarns and needle sizes to achieve the desired outcome. Happy knitting!
Deciding on a Pattern Design and Size
When it comes to knitting, the first step in creating a knit pattern is deciding on the design and size of your project. This decision will depend on several factors, including your skill level, the intended use of the finished item, and personal preferences.
To begin, consider the type of item you want to knit. Are you interested in making a sweater, a scarf, a hat, or perhaps a blanket? Each item has its own unique design considerations, so it’s important to choose something that aligns with your skill level and interests.
Next, think about the size of the finished item. If you’re making a garment, take measurements of the person who will be wearing it to ensure a proper fit. Consider the desired ease or fit style as well – do you want a tight-fitting sweater or a looser, more relaxed fit?
Once you have a general idea of the design and size, you can start exploring pattern options. You can find patterns in knitting books, magazines, or online resources. Many websites offer a wide range of free patterns for all skill levels. Look for patterns that include clear instructions and illustrations or photos to help guide you through the knitting process.
If you’re a beginner, it may be helpful to start with a simple pattern that uses basic stitches and techniques. As you gain more experience and confidence, you can gradually tackle more complex patterns with intricate stitch patterns and shaping.
Consider also the yarn weight and fiber content when choosing a pattern. Different yarns will yield different results, so be sure to choose a pattern that complements the yarn you have in mind.
It’s also a good idea to make a gauge swatch before starting your project to ensure that your stitch and row count match the pattern. This will help you avoid any surprises in sizing or fit.
Lastly, don’t be afraid to modify patterns to suit your preferences or needs. Knitting is a creative craft, and you can always add your own personal touch to a pattern. Just make sure to take accurate notes of any modifications you make, so you can replicate your changes if needed.
By carefully considering the design, size, and other factors, you can choose a knit pattern that is both enjoyable to knit and results in a beautiful finished item.
Understanding Knit Stitch and Purl Stitch
When it comes to knitting, there are two basic stitches that you need to understand: the knit stitch and the purl stitch. These two stitches are the building blocks of almost all knitting patterns, so it’s important to know how they work.
Knit Stitch:
The knit stitch is the most basic stitch in knitting. It creates a smooth, V-shaped pattern on the right side of your work. To knit, you insert the right-hand needle into the front of the next stitch on the left-hand needle, from left to right. Then, wrap the yarn around the right-hand needle counterclockwise, and pull it through the stitch, slipping the new stitch onto the right-hand needle.
Purl Stitch:
The purl stitch is similar to the knit stitch, but it creates a bumpy, horizontal pattern on the right side of your work. To purl, you insert the right-hand needle into the front of the next stitch on the left-hand needle, from right to left. Then, wrap the yarn around the right-hand needle clockwise, and pull it through the stitch, slipping the new stitch onto the right-hand needle.
It’s important to note that the knit stitch and the purl stitch are essentially the same stitch, just worked in opposite directions. When you knit on one row, you will purl on the next row to create a stockinette stitch pattern. By alternating these two stitches, you can create a wide variety of textures and patterns in your knitting.
Tips for working with knit and purl stitches:
- Keep your tension consistent to ensure even stitches.
- Make sure to insert the needle correctly into the stitch to avoid twisting it.
- Practice on a swatch or a small project to get comfortable with these stitches before starting a larger project.
- Use stitch markers to help you keep track of where you are in a pattern.
Now that you understand the basic knit and purl stitches, you’re ready to start exploring more advanced knitting techniques and patterns. Remember, practice makes perfect, so keep knitting and experimenting to improve your skills!
Creating a Gauge Swatch
Before starting any knitting project, it’s important to create a gauge swatch. This small sample of your knitting will help you determine the correct tension for your pattern and ensure that your finished project will be the right size.
Here are the steps to create a gauge swatch:
- Choose your yarn and needles: Select the yarn and needles recommended by your pattern. The gauge stated in the pattern is based on a specific yarn and needle size, so it’s important to match them as closely as possible.
- Make a basic swatch: Cast on a few more stitches than the recommended gauge width and knit a few rows in the specified stitch pattern. This will give you a larger area to measure and help eliminate any inconsistencies at the edges of your swatch.
- Measure your swatch: Using a ruler or tape measure, measure the width and height of your knitted swatch. Make sure to measure the area without stretching or distorting the stitches.
- Calculate your gauge: Divide the number of stitches across the width of your swatch by the measurement in inches. This will give you your stitch gauge. Do the same for the number of rows in the height of your swatch to determine your row gauge.
- Compare with the pattern: Check your stitch and row gauge against the gauge stated in your pattern. If your gauge matches, congratulations! You can proceed with your project. If your gauge is different, you may need to adjust your needle size to achieve the correct tension. A smaller needle size will result in more stitches per inch, while a larger needle size will result in fewer stitches per inch.
Remember, creating a gauge swatch is essential for any knitting project, as it allows you to achieve the correct size and fit. Taking the time to measure and adjust your tension will ensure that your finished piece matches the pattern’s specifications.
Casting on and Knitting the First Rows
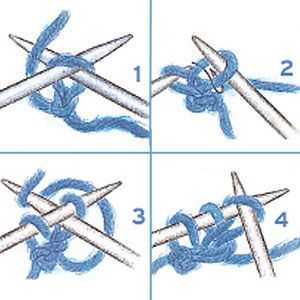
Before you start knitting, you need to cast on your stitches. Casting on is the process of creating the first row of stitches on your knitting needle. There are several methods you can use to cast on, but the most common method for beginners is the long-tail cast on.
To do the long-tail cast on, start by making a slipknot at the end of your working yarn. Then, hold the slipknot in your right hand and place the knitting needle in your left hand.
Next, make a loop with the working yarn using your left thumb and index finger. Insert the knitting needle through the loop from front to back, and then bring the needle under the loop and over the yarn tail.
With your right hand, pull the yarn tail to tighten the stitch on the needle. Repeat this process until you have cast on the desired number of stitches.
Once you have cast on your stitches, you are ready to start knitting the first rows of your pattern. This is done by inserting the right-hand needle into the first stitch on the left-hand needle, from left to right.
Hold the working yarn in your right hand, behind the needles. Wrap the yarn around the right-hand needle, moving it counterclockwise. Then, use the right-hand needle to pull the yarn through the first stitch, creating a new loop.
Slide the original stitch off the left-hand needle, and the new stitch will now be on the right-hand needle. Repeat this process for each stitch on the left-hand needle until you have knitted all the stitches.
Continue knitting the subsequent rows by repeating the same process. Remember to always keep the working yarn behind the needles and to wrap it counterclockwise around the right-hand needle before pulling it through the stitch.
As you knit more rows, you will start to see the pattern forming. Don’t worry if your knitting looks uneven or messy at first – practice makes perfect! As you gain more experience, your stitches will become more even and your knitting will look more neat and professional.
Now that you know how to cast on and knit the first rows, you are ready to start working on your knit pattern. Remember to take your time, be patient with yourself, and enjoy the process of creating something beautiful with your own two hands.
Adding Variation with Different Stitches
One of the great things about knitting is that there are so many different stitches and techniques you can use to add variation and interest to your knit patterns. Here are some popular stitches to try:
- Garter Stitch: This is one of the simplest stitches and is perfect for beginners. It is created by knitting every row, resulting in a bumpy texture.
- Stockinette Stitch: This stitch is created by alternating rows of knitting and purling. It creates a smooth, flat fabric with a distinct right side and wrong side.
- Ribbing: Ribbing is a common stitch pattern used for cuffs, hems, and collars. It is created by alternately knitting and purling stitches in the same row, giving the fabric a stretchy, textured look.
- Seed Stitch: This stitch pattern creates a bumpy texture similar to garter stitch but with a more intricate look. It is created by alternating knit and purl stitches within the same row.
- Cable Stitch: Cables are a popular stitch pattern that create a twisted, braided effect. They can be simple or complex, depending on the number of stitches and rows involved.
By incorporating different stitches and techniques into your knit patterns, you can create unique textures and designs. Don’t be afraid to experiment and try out new stitches to add variety and interest to your knitting projects!
Shaping Your Knit Project with Increases and Decreases
When knitting a project, one of the important aspects to consider is shaping. Shaping helps give your project structure and allows it to fit properly. Increases and decreases are commonly used techniques to shape your knit project.
Increases
Increases are stitches that are added to your project, increasing the overall stitch count. They help create a larger fabric by adding width and fullness. Here are a few common types of increases:
- Knit Front and Back (KFB): This increase is created by knitting into the front of a stitch, then into the back of the same stitch. This creates a new stitch and increases the stitch count by one.
- Make One (M1): This increase involves picking up the horizontal strand of yarn between two stitches, inserting the needle from the front to the back, and knitting into the back loop. This creates a new stitch.
- Yarn Over (YO): This increase is made by simply bringing the yarn forward between the needles and knitting the next stitch. The yarn over creates a new stitch and an eyelet hole in the fabric.
Decreases
Decreases are stitches that are removed from your project, decreasing the overall stitch count. They help create shaping by eliminating stitches, resulting in a more fitted look. Here are a few common types of decreases:
- K2tog (Knit Two Together): This decrease involves knitting two stitches together as if they were one. This decreases the stitch count by one.
- SSK (Slip Slip Knit): This decrease is created by slipping two stitches individually as if to knit, then knitting them together through the back loops. This also decreases the stitch count by one.
- Slip 1, Knit 1, Pass Slipped Stitch Over (SKP): This decrease involves slipping one stitch knitwise, knitting the next stitch, and then passing the slipped stitch over the knit stitch. This decreases the stitch count by one.
By combining different types of increases and decreases, you can create a variety of shaping patterns in your knit projects. It’s essential to follow the pattern instructions and use the correct increase and decrease techniques to achieve the desired shape.
Remember to always count your stitches after working an increase or decrease row to ensure you have the correct stitch count for the next section of your project. Happy knitting!
Finishing Your Knit Project and Blocking
Once you’ve completed knitting your project, there are a few important steps to take to finish it off and ensure that it looks its best. One of these crucial steps is blocking.
Blocking:
- Blocking is the process of shaping your knit project to the correct measurements and allowing the stitches to relax and settle into place.
- It can help even out tension and make your finished project look more professional.
- To block your project, you will need to wet it first by soaking it in a basin of lukewarm water with a gentle wool wash or mild detergent.
- After soaking, gently squeeze out excess water without wringing or twisting.
- Next, lay your project flat on a clean, dry towel and roll it up to remove even more water.
- Finally, lay your project out on a blocking board or surface, shaping it to the correct measurements and pinning it in place with rust-proof T-pins or blocking wires.
- Allow your project to dry completely before unpinning.
Finishing:
- Before blocking, it’s important to finish your project by weaving in all loose ends.
- Use a tapestry needle or crochet hook to carefully weave the ends into the back of your work, making sure they are secure and won’t come undone with wear.
- If your project has seams, use a mattress stitch or another appropriate seaming method to join the pieces together neatly.
- Once blocking and finishing are complete, your knit project is ready to be enjoyed or gifted!
Remember, blocking and finishing may take some extra time, but they can make a big difference in the final appearance and longevity of your knit project. Don’t skip these important steps!
FAQ:
What materials do I need to make a knit pattern?
To make a knit pattern, you will need yarn, knitting needles, a tape measure, scissors, and a stitch marker.
Can I use any type of yarn for a knit pattern?
Yes, you can use different types of yarn for a knit pattern. The choice of yarn will depend on the pattern you are making and the desired outcome.
How do I choose the right size for my knit pattern?
To choose the right size for your knit pattern, you can refer to the pattern’s sizing guide. You can also measure your body and compare it to the measurements provided in the pattern to ensure a proper fit.
What are some beginner-friendly knit patterns?
Some beginner-friendly knit patterns include scarves, hats, and simple blankets. These patterns usually involve basic knit and purl stitches and are great for practicing the fundamentals of knitting.
What are some tips for reading a knit pattern?
When reading a knit pattern, it is important to carefully read the instructions and abbreviations. It can be helpful to highlight or mark important sections of the pattern. It is also important to understand the gauge and to check your tension as you work to ensure accurate results.