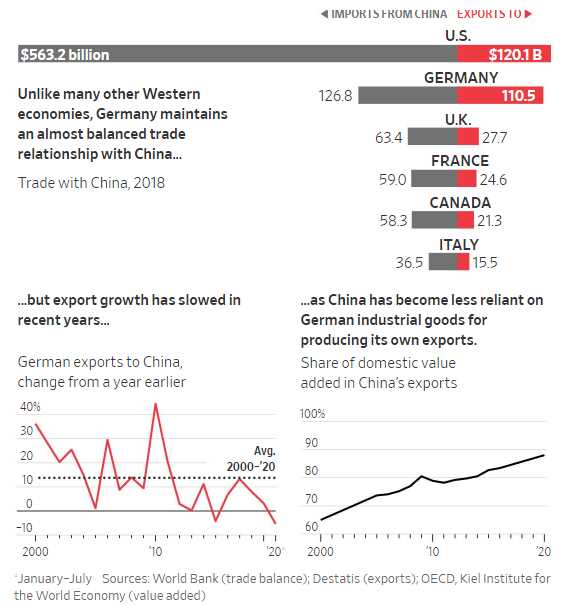
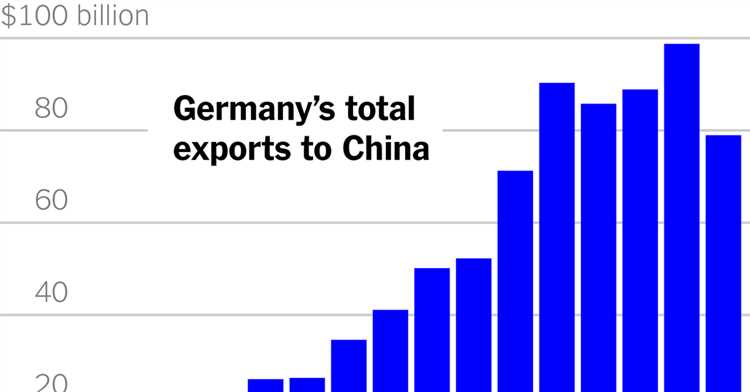
Germany and China are two economic powerhouses that have had a significant impact on the global economy. Both countries are known for their thriving industries, technological advancements, and strong export economies. However, when it comes to measuring their wealth, it can be difficult to determine which country is richer.
Germany is known for its highly developed and diversified economy. It is one of the largest exporters in the world and is home to many globally recognized companies such as Volkswagen, BMW, and Siemens. The country has a strong focus on manufacturing, with industries such as automotive, machinery, and chemical production leading the way. Germany’s economy is also known for its well-developed infrastructure, highly skilled workforce, and strong social welfare system.
On the other hand, China has experienced rapid economic growth over the past few decades. The country’s economy is primarily driven by manufacturing and exports, with industries such as electronics, textiles, and automobile production playing a significant role. China is also home to a large consumer market, with a population of over 1.4 billion people. Additionally, the country has made significant investments in infrastructure development and technological innovation.
While Germany has a higher GDP per capita compared to China, it is important to consider other factors when comparing their wealth. China has a much larger population and a growing middle class, which contributes to its overall economic power. Additionally, China has been investing heavily in research and development, and is becoming a global leader in technology and innovation. However, Germany has a more stable and well-established economy, with a strong focus on high-quality manufacturing and exports.
In conclusion, comparing the wealth of Germany and China is a complex task. While Germany may have a higher GDP per capita, China’s large population and rapid economic growth cannot be discounted. Both countries have their strengths and weaknesses, and their economic power is evident in different ways. Ultimately, it is important to look beyond GDP numbers and consider other factors when evaluating the wealth of these economic powerhouses.
Is Germany richer than China?
When it comes to comparing the economic powerhouses of Germany and China, it is important to consider various factors such as GDP, GDP per capita, and purchasing power parity (PPP). These indicators provide insights into the overall wealth and economic strength of a country.
Germany, known for its strong automotive industry and manufacturing sector, has a high GDP and is often considered one of the wealthiest countries in Europe. In 2020, Germany’s GDP was approximately $3.85 trillion, making it the fourth-largest economy in the world.
On the other hand, China, with its massive population and rapid economic growth, has become the second-largest economy globally. In 2020, China’s GDP was approximately $14.34 trillion, more than triple that of Germany.
However, comparing GDP alone may not provide a complete picture of a country’s wealth. GDP per capita is another important indicator, as it considers the population size of a country. Germany has a smaller population compared to China, so when we look at GDP per capita, Germany’s figure is much higher. In 2020, Germany’s GDP per capita was approximately $46,279, while China’s GDP per capita was around $10,262.
Additionally, purchasing power parity (PPP) adjusts GDP per capita based on the cost of living and the purchasing power of a country’s currency. When considering PPP, Germany still has a higher figure compared to China. Germany’s PPP GDP per capita in 2020 was approximately $57,905, while China’s was around $18,620.
It is essential to note that these figures are subject to fluctuations and can change over time. Additionally, they may not reflect the overall well-being or happiness of a country’s population. It is crucial to consider various aspects when comparing the economic power and wealth of two countries.
In conclusion, while Germany is considered one of the wealthiest countries in Europe, China’s massive population and rapid economic growth have enabled it to become the second-largest economy globally. Considering GDP per capita and purchasing power parity, Germany has a higher figure compared to China. However, comparing the wealth and economic power of two countries is a complex matter that requires analyzing multiple indicators beyond just GDP.
Comparing the economic powerhouses
When it comes to comparing economic powerhouses, both Germany and China stand out as major players on the global stage. Each country possesses unique strengths and challenges, making them fascinating subjects for comparison.
Economic Size and GDP
Germany, with its highly advanced industrial sector and robust export-oriented economy, has long been recognized as one of the wealthiest countries in the world. Its gross domestic product (GDP) stands at over $3.8 trillion (2019), making it the fourth-largest economy globally.
On the other hand, China, the most populous country in the world, has experienced rapid economic growth over the past few decades. Its GDP has surpassed $14.3 trillion (2019), making it the second-largest economy in the world, and the largest in terms of purchasing power parity (PPP).
Per Capita Income and Wealth Distribution
While China outperforms Germany in terms of total GDP, it falls behind in terms of per capita income. Germany boasts a higher per capita income due to its smaller population and more equitable wealth distribution system. In Germany, the average income per person is around $47,600, compared to China’s average income of about $10,100 per person.
Furthermore, Germany maintains a relatively low level of income inequality compared to China. Germany has a Gini coefficient of around 0.29, indicating a more equal distribution of wealth, while China has a Gini coefficient of around 0.47, suggesting a higher level of income inequality.
Trade and Exports
Both Germany and China are major players in international trade, but Germany has traditionally been more export-oriented. Germany is known for its prowess in manufacturing and exports a wide range of high-quality goods, such as automobiles, machinery, and chemical products. In 2019, Germany’s total exports amounted to $1.49 trillion.
China, on the other hand, has become the world’s largest exporter due to its massive manufacturing capacity and low production costs. China exports a wide range of products, including electronics, textiles, and machinery. In 2019, China’s total exports reached $2.5 trillion.
Conclusion
When comparing Germany and China as economic powerhouses, it’s important to consider various factors such as GDP, per capita income, wealth distribution, and trade. While Germany has a smaller economy compared to China, it boasts a higher per capita income and a more equal distribution of wealth. In terms of trade, both countries play significant roles in the global market.
Overall, Germany and China are unique economic powerhouses with their own strengths and challenges, contributing to the global economy in different ways.
Overview of the economies
Germany and China are two economic powerhouses that play a significant role in the global economy. Both countries have highly developed economies, but they have different strengths and characteristics.
Germany:
- Germany is known for its strong manufacturing sector, particularly in automobile production. It is home to several world-renowned automobile manufacturers such as BMW, Volkswagen, and Mercedes-Benz.
- The country has a highly skilled workforce and is highly regarded for its engineering and technical expertise.
- Germany has a well-developed infrastructure, including a modern transportation system and efficient logistics networks, which supports its export-oriented economy.
- The country is also known for its robust financial services sector, with Frankfurt being a major financial hub in Europe.
- Germany has a high standard of living and a well-developed social welfare system that provides a strong safety net for its citizens.
China:
- China has the world’s largest population, which contributes to its significant consumer market and labor force.
- The country has experienced rapid economic growth over the past few decades, becoming the world’s second-largest economy.
- China is a major manufacturing powerhouse, producing a wide range of goods including electronics, textiles, and machinery.
- The country has a strong focus on infrastructure development, with extensive investments in transportation, energy, and telecommunications.
- China is also one of the largest exporters in the world, benefiting from its low-cost labor and competitive manufacturing sector.
- The country has a growing middle class and an increasing consumer demand, which is driving domestic consumption and economic growth.
In summary, Germany and China have different economic strengths and characteristics. Germany is known for its strong manufacturing sector, skilled workforce, and well-developed infrastructure. China, on the other hand, has the advantage of a large consumer market, low-cost labor, and a focus on infrastructure development. Both countries contribute significantly to the global economy and play important roles in different sectors.
Germany: A European Economic Powerhouse
Germany is one of the leading economies in Europe and a global economic powerhouse. It is known for its robust industrial sector, technological advancements, and strong export-oriented economy.
Industrial prowess:
- Germany is renowned for its strong manufacturing sector, which contributes significantly to its economic growth. Industries such as automotive, machinery, chemicals, and electronics are key drivers of the German economy.
- The country’s engineering and technological expertise have made it a leader in innovative and high-quality products, ensuring a competitive advantage in the global market.
Export-oriented economy:
- Germany is consistently one of the world’s largest exporters, trading goods and services globally. Its well-established infrastructure and logistics network facilitate efficient trade.
- The automotive industry, with well-known brands such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volkswagen, plays a crucial role in Germany’s export economy.
Financial stability:
- Germany has a stable financial system, characterized by strong banks and prudent fiscal policies. The country’s commitment to fiscal discipline has helped maintain investor confidence and attract foreign investment.
- Germany is also home to several globally recognized financial institutions, such as Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank, further contributing to its financial strength.
Skilled workforce:
- Germany is known for its highly skilled and educated workforce, thanks to its emphasis on vocational training and apprenticeship programs. This ensures a steady supply of qualified workers for its industries.
- The country’s education system is renowned for its focus on technical and scientific disciplines, providing a solid foundation for innovation and productivity.
Investment in research and development:
- Germany is committed to investing in research and development, fostering innovation and technological advancements. This focus on R&D has helped maintain the country’s competitiveness in various industries.
- The presence of prestigious research institutions and universities contributes to Germany’s reputation as an innovation hub.
In summary, Germany’s economic strength lies in its strong manufacturing sector, export-oriented economy, financial stability, skilled workforce, and commitment to research and development. These factors have propelled Germany to become one of the most influential economic powerhouses in Europe and the world.
China: The rising giant
China is often referred to as the “rising giant” in the context of economic powerhouses. Its immense population, rapidly growing economy, and advancements in technology have positioned it as one of the most influential countries in the global economy.
With a population of over 1.4 billion people, China holds the title for the most populous country in the world. This vast population provides a significant workforce, enabling China to be a manufacturing powerhouse. The country’s large labor force, combined with its low labor costs, has made it an attractive destination for multinational corporations to set up production plants.
China’s economic growth has been remarkable over the past few decades. The country’s GDP has consistently experienced double-digit growth, making it the second-largest economy in the world after the United States. China’s economic success has been primarily driven by its focus on export-oriented industries, including electronics, textiles, and machinery.
In addition to its manufacturing prowess, China has made significant investments in research and development. The country is striving to become a global leader in technology and innovation. Chinese companies, such as Huawei and Alibaba, have become major players in the tech industry and have expanded their operations globally.
China’s rising economic power has not gone unnoticed by the international community. The country has become a key player in international trade and has established economic partnerships with countries around the world. Its influence on global economic policies has been increasing, challenging the traditional dominance of Western economies.
Despite its economic strength, China still faces challenges. The country grapples with income inequality, environmental pollution, and an aging population. However, the Chinese government has implemented various measures to address these issues and continue its economic growth trajectory.
In summary, China’s immense population, rapid economic growth, and technological advancements have positioned it as a rising giant in the global economy. With its influence continuing to grow, China is expected to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of the global economy.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the economic output of a country. It represents the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period of time, usually a year. GDP is commonly used to compare and analyze the economic performance of different countries.
In the case of Germany, as of 2020, its GDP was approximately $3.8 trillion, making it the largest economy in Europe and the fourth largest in the world. Germany has a highly developed and diversified economy, with strong sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, engineering, and finance.
On the other hand, China’s GDP in 2020 was approximately $15.42 trillion, making it the second largest economy in the world. China has experienced rapid economic growth over the past few decades, propelled by its vast population, manufacturing prowess, and increasing consumer demand.
While Germany has a higher GDP per capita compared to China, indicating a higher standard of living for its citizens, China’s sheer scale and size make it a formidable economic powerhouse. China’s GDP growth rate has consistently outpaced that of Germany and many other advanced economies, positioning it as a major player in the global economy.
In terms of GDP composition, Germany relies heavily on exports, with a strong focus on high-quality manufacturing and engineering. China, on the other hand, has a more diverse economy, with manufacturing, services, and construction sectors playing significant roles.
| Germany | China | |
|---|---|---|
| GDP (2020) | $3.8 trillion | $15.42 trillion |
| GDP per capita (2020) | $45,466 | $10,716 |
| GDP growth rate (2020) | -5.0% | 2.3% |
Overall, both Germany and China are influential players in the global economy, each with their unique strengths and characteristics. While Germany excels in high-quality manufacturing and engineering, China’s scale, growth rate, and diversification make it one of the fastest-growing economies in the world.
Germany’s GDP: A strong and stable growth
Germany has established itself as one of the world’s leading economies, with a GDP that consistently demonstrates strong and stable growth. The country’s robust economy is driven by several key factors, including its highly skilled workforce, advanced infrastructure, and diverse industrial sectors.
Germany’s GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, measures the value of all goods and services produced within the country over a specific period. In recent years, Germany has consistently ranked among the top economies in the world, positioning itself as an economic powerhouse.
One of the key drivers of Germany’s strong GDP growth is its highly skilled and educated workforce. The country has a well-established education system that focuses on technical and vocational training, ensuring a steady supply of qualified and skilled workers. This has led to a highly productive workforce that contributes significantly to the country’s economic output.
Germany’s advanced infrastructure also plays a crucial role in its economic success. The country has a well-developed transport network, including an extensive railway system and modern highways, facilitating the movement of goods and services within and beyond its borders. Additionally, Germany has invested heavily in renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, further supporting its sustainable development and economic growth.
The country’s industrial sectors, including automotive, engineering, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals, contribute significantly to its GDP. Germany is known for its high-quality and innovative products, which enjoy a strong demand both domestically and internationally. Global brands such as Volkswagen, BMW, and Mercedes-Benz have their roots in Germany, further bolstering the country’s economic performance.
Germany’s commitment to research and development also fuels its economic growth. The country invests heavily in scientific research and technological advancements, creating a favorable environment for innovation and attracting foreign investment. As a result, Germany remains at the forefront of technological advancements and is well-positioned to maintain its economic dominance.
In conclusion, Germany’s GDP continues to demonstrate strong and stable growth, fueled by factors such as its highly skilled workforce, advanced infrastructure, diverse industrial sectors, and commitment to research and development. These factors have solidified Germany’s position as one of the world’s leading economic powerhouses.
China’s GDP: The rapid expansion
In recent decades, China has experienced a remarkable expansion in its Gross Domestic Product (GDP), solidifying its position as one of the world’s economic powerhouses. Rapid industrialization, modernization, and massive investment in infrastructure have played a significant role in driving the growth of China’s economy.
China’s GDP has been growing at an impressive pace, with average annual growth rates exceeding 9% over the past 40 years. This remarkable growth has been fueled by several factors, including large-scale manufacturing, export-oriented policies, and increased domestic consumption.
One of the key drivers of China’s economic growth has been its manufacturing sector, which has become a global manufacturing hub. With a vast labor force and a competitive advantage in terms of cost, China has attracted numerous foreign companies to set up their factories within its borders, thereby boosting its GDP.
Furthermore, China has adopted export-oriented policies, which have helped it to become the world’s largest exporter of goods. The country has been able to capitalize on its low production costs, as well as its efficient logistics and transportation infrastructure, to dominate global export markets.
In recent years, China has also witnessed a significant increase in domestic consumption. With a population of over 1.4 billion people, the rising middle class has fueled demand for a wide range of goods and services, contributing to the expansion of China’s economy.
In addition to these drivers, China has made considerable investments in infrastructure development. The country has undertaken large-scale projects such as high-speed railways, urbanization initiatives, and the construction of mega-cities. These investments have not only created employment opportunities but have also stimulated economic growth.
China’s rapid expansion has also been accompanied by challenges. The country has experienced a widening income gap, environmental issues, and an aging population. However, the Chinese government has been taking measures to address these challenges and ensure the sustainability of its economic growth.
In conclusion, China’s GDP has experienced a rapid expansion due to factors such as rapid industrialization, export-oriented policies, increased domestic consumption, and massive investments in infrastructure. While the country faces challenges, its remarkable economic growth has solidified its position as a global economic powerhouse.
Per capita income
When comparing the per capita income of Germany and China, it is important to consider the vast difference in population size between the two countries. As of 2020, Germany has a population of approximately 83 million people, while China boasts a population of over 1.4 billion people.
In terms of per capita income, Germany generally outperforms China. According to the World Bank, Germany had a per capita income of $53,340 in 2019, making it one of the highest in the world. In contrast, China’s per capita income was $10,410 in the same year.
This significant difference can be attributed to various factors, including the level of economic development, industrialization, and income distribution within each country.
Germany has a highly-developed and diversified economy, known for its technological advancements, innovation, and strong manufacturing sector. The country also benefits from a highly skilled workforce and a strong social welfare system, which contributes to a higher standard of living for its citizens.
On the other hand, China is a rapidly developing country that has experienced significant economic growth over the past few decades. However, it still faces challenges such as income inequality and a large rural population engaged in agriculture. These factors contribute to a lower per capita income compared to Germany.
It is important to note that per capita income alone does not provide a complete picture of the overall economic well-being of a country. Other factors such as the cost of living, access to essential services, and quality of life should also be taken into consideration.
In conclusion, Germany generally has a higher per capita income compared to China. However, it is crucial to consider the context of the vast disparities in population and the unique economic and social characteristics of each country when making such comparisons.
Germany: Higher individual wealth
In terms of individual wealth, Germany ranks higher than China. With a higher per capita income, Germans generally enjoy a higher standard of living and a better quality of life.
Germany’s strong economy and well-developed social welfare system contribute to its high individual wealth. The country has a highly skilled workforce, robust manufacturing sector, and a strong focus on innovation and technology.
Germany also has a relatively equal distribution of wealth, with a lower level of income inequality compared to many other countries. This means that a larger portion of the population can benefit from the nation’s economic success.
The country has a high standard of healthcare, education, and social security, ensuring that its citizens have access to the necessary resources and support they need.
Additionally, Germany has a low poverty rate and a high level of economic mobility. This means that individuals have a better chance of improving their economic status and achieving upward mobility.
Overall, Germany’s higher individual wealth is a result of its strong economy, social welfare system, and commitment to providing a high standard of living for its citizens.
FAQ:
Is Germany wealthier than China?
Germany is not wealthier than China in terms of overall GDP. China has the second-largest economy in the world, while Germany ranks fourth. However, when it comes to per capita income, Germany has a higher average income than China.
What are the main reasons for China’s economic growth?
China’s economic growth can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, its rapid industrialization and urbanization have played a significant role in boosting its economy. Additionally, China’s large population has provided a huge internal market for its goods and services. Foreign direct investment and export-oriented policies have also contributed to its economic growth.
What industries are contributing to Germany’s economy?
Germany has a diverse and highly developed economy, with several key industries contributing to its overall economic strength. The automotive industry, including companies like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Volkswagen, is a major contributor. Germany is also known for its machinery, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries. Additionally, the country has a strong financial sector.
Which country has a higher GDP growth rate: Germany or China?
China has consistently had a higher GDP growth rate compared to Germany in recent years. While Germany has experienced steady economic growth, China’s GDP growth rate has been much higher due to its large-scale infrastructure investments, rapid industrialization, and urbanization. However, it’s important to note that China’s economic growth rate has been gradually slowing down in recent years.