Weaving and knitting are two ancient textile techniques that have been used for centuries to create beautiful and functional fabrics. While both methods involve interlacing yarns to form a fabric, there are significant differences in the process and end result. In this article, we will compare weaving and knitting, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and which technique may be the best for different projects.
Weaving is a technique that involves interlacing two sets of yarns – the warp and the weft. The warp threads are stretched vertically on a loom, while the weft threads are woven horizontally through the warp. The result is a fabric with a strong structure and distinct patterns. Weaving allows for precise control over the appearance and texture of the fabric, making it ideal for creating intricate designs and motifs.
Knitting, on the other hand, involves interlocking loops of yarn with knitting needles or a machine. This technique creates a stretchy and flexible fabric that is great for garments and accessories. Knitting offers a wide range of stitch patterns and textures, allowing for endless possibilities in design. It is also a more portable and versatile technique, as it does not require a large loom and can be done by hand or with the help of a machine.
When considering which technique is the best, it ultimately depends on the project and desired outcome. Weaving is best for creating structured fabrics with intricate patterns, such as tapestries, rugs, and home decor items. Knitting, on the other hand, is perfect for creating garments, accessories, and soft furnishings. Both techniques require skill and practice to master, but with dedication and creativity, the possibilities are endless.
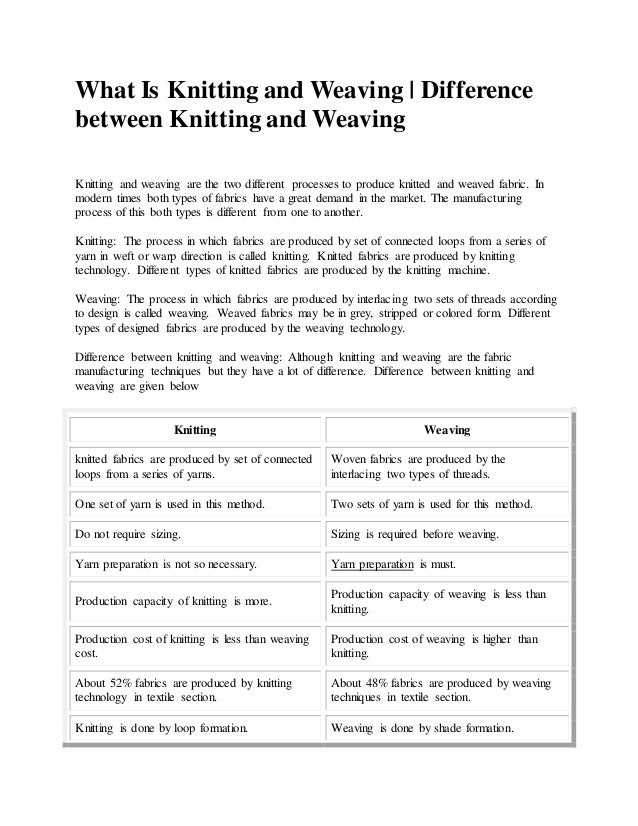
Differences between Weaving and Knitting
1. Technique:
- Weaving: Weaving is a technique in which two sets of threads, called the warp and the weft, are interlaced to create a fabric. The warp threads run vertically on a loom, while the weft threads are woven horizontally.
- Knitting: Knitting is a technique in which loops of yarn are interlaced to create a fabric. The loops are formed using two knitting needles, and each loop is pulled through the next loop, creating a chain.
2. Tools:
- Weaving: Weaving requires a loom, which is a device that holds the warp threads taut and provides a structure for interlacing the weft threads. Various types of looms can be used, including floor looms, table looms, and rigid heddle looms.
- Knitting: Knitting requires two knitting needles, typically made of metal, plastic, or wood. There are different types and sizes of knitting needles available, depending on the desired gauge and thickness of the fabric.
3. Fabric:
- Weaving: Weaving produces a fabric that has a more structured and stable appearance. The interlacing of the warp and weft threads creates a strong and durable fabric, which is commonly used for garments, home furnishings, and accessories.
- Knitting: Knitting produces a fabric that is more flexible and stretchy. The loops of yarn create a fabric with a natural elasticity, making it suitable for items that require stretch, such as sweaters, socks, and hats.
4. Versatility:
- Weaving: Weaving allows for intricate patterns and designs to be created by manipulating the warp and weft threads. Different weaving techniques, such as plain weave, twill weave, and satin weave, can be employed to achieve various textures and finishes.
- Knitting: Knitting also allows for a wide range of patterns and designs to be created, by varying the types of stitches and colors used. Knitting can be done in plain stitch, purl stitch, rib stitch, cable stitch, and many other stitch patterns.
| Aspect | Weaving | Knitting |
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Interlacing warp and weft threads | Interlacing loops of yarn |
| Tools | Loom | Knitting needles |
| Fabric | Structured and stable | Flexible and stretchy |
| Versatility | Intricate patterns and designs | Various stitch patterns and colors |
Historical Background of Weaving and Knitting
Weaving and knitting are two ancient techniques of textile production that have been practiced for thousands of years. While both methods involve the creation of fabric from thread, they differ in their processes and historical origins.
Weaving:
Weaving is believed to have originated around 6000 BCE in ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Egypt. It involves the interlacing of two sets of threads, known as the warp and weft, to create a stable fabric structure. The warp threads are stretched vertically on a loom, while the weft threads are woven horizontally through the warp, creating a tightly woven fabric.
Throughout history, weaving has played a crucial role in the development of societies, as it allowed for the production of clothing, household items, and even sails for ships. It was often a labor-intensive process, carried out by skilled artisans and often facilitated the growth of trade and commerce.
Over time, weaving techniques evolved, and different types of looms were developed to increase the efficiency and complexity of the weaving process. Examples include the horizontal ground loom, the backstrap loom, and the Jacquard loom, which used punched cards to control the weaving pattern.
Knitting:
The origins of knitting are less clear than weaving, but it is believed to have begun around the 3rd or 4th century BCE in the Middle East. Unlike weaving, knitting involves the interlocking of loops of yarn using knitting needles or a knitting machine to create fabric.
Knitting was initially used for practical purposes, such as creating warm clothing and accessories. However, it also became an important art form and a means of self-expression. Knitting patterns and techniques varied across different cultures and regions, and knowledge of knitting was often passed down through generations.
In the Middle Ages, knitting guilds were established in Europe, and the art of knitting became more formalized. Knitting techniques and tools continued to evolve, with the introduction of circular knitting needles and knitting machines in the 19th century.
Conclusion:
Weaving and knitting have deep historical roots and have been important textile production techniques throughout human history. Both methods have their unique characteristics and applications, and the choice between them depends on factors such as fabric type, desired appearance, and personal preference.
Advantages of Weaving over Knitting
Weaving is a traditional technique of creating fabrics by interlacing threads or yarns at right angles. While knitting is another technique that involves creating fabrics by loops of yarns, weaving offers several advantages over knitting. These advantages include:
- Structural Stability: Weaving creates a more stable and durable fabric compared to knitting. The interlacing of threads in weaving results in a tighter and more structured fabric, which is less prone to stretching or losing shape over time.
- Uniformity: Weaving produces a more uniform fabric with consistent tension and thickness. This uniformity makes woven fabrics suitable for structured garments and projects that require precise measurements.
- Versatility: Weaving allows for greater flexibility in terms of design options. Different patterns, colors, and textures can be easily achieved through various weaving techniques and the use of different types of yarns.
- Wider Width: Weaving enables the production of wider fabrics compared to knitting. This makes it a preferable technique for creating larger textiles such as blankets, curtains, and upholstery.
- Ability to Weave Complex Designs: Weaving offers more control and precision when it comes to creating intricate patterns and designs. This makes it a preferred choice for complex projects that require detailed motifs or images.
- Less Elasticity: Weaving creates fabrics with less elasticity compared to knitting. This property can be advantageous in projects where a stretchy fabric is not desired, such as in bags or rugs.
In conclusion, while both weaving and knitting have their merits, weaving offers distinct advantages in terms of structural stability, uniformity, versatility, wider width options, ability to weave complex designs, and less elasticity. These advantages make weaving a preferred technique for various textile applications.
Advantages of Knitting over Weaving
1. Portability: Knitting is much more portable than weaving. With just a pair of knitting needles and a ball of yarn, you can easily take your project with you wherever you go. This is especially advantageous for people who travel frequently or enjoy knitting on the go.
2. Versatility: Knitting allows for a wide range of patterns and stitch types, enabling you to create intricate designs and textures in your projects. This versatility allows knitters to experiment with various techniques and create unique and personalized pieces.
3. Flexibility: Unlike weaving, knitting offers flexibility in terms of the size and shape of the project. Knitting allows you to easily add or remove stitches, alter the size of your project, and create three-dimensional items such as hats, socks, and stuffed animals.
4. Speed: Knitting is generally faster than weaving, as you only work with one or a few stitches at a time. This makes it a more efficient technique for creating projects in a shorter amount of time.
5. Creativity: Knitting allows for more creative expression, as you can easily combine different yarn colors and textures to create unique and visually appealing projects. The ability to create complex patterns and textures through knitting also adds to the creative possibilities.
6. Accessibility: Knitting is generally easier to learn and master compared to weaving. The basic knitting stitch is simple and can be easily picked up by beginners. Additionally, there are numerous resources available, such as books, online tutorials, and knitting communities, that provide support and guidance for knitters of all skill levels.
7. Cost: Knitting can be a more cost-effective hobby compared to weaving. It requires minimal equipment, mainly consisting of knitting needles and yarn, which are generally more affordable than weaving looms and tools.
In conclusion, while both weaving and knitting have their own advantages and appeal, knitting offers portability, versatility, flexibility, speed, creativity, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness that make it a preferred technique for many crafters.
Comparison of Weaving and Knitting in Terms of Durability
Weaving and knitting are two different techniques used to produce fabrics. Each technique has its own characteristics and advantages, including durability. In terms of durability, both weaving and knitting have their pros and cons.
Weaving:
- Stability: Weaving creates a stable and strong fabric due to the interlocking of warp and weft yarns. The structure of woven fabrics makes them less likely to stretch or deform over time.
- Tensile Strength: Woven fabrics generally have high tensile strength, making them more resistant to tearing and breaking. This makes woven fabrics suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as upholstery and industrial use.
- Longevity: Woven fabrics are known for their longevity. They can withstand repeated use, washing, and general wear and tear without losing their shape or strength.
- Maintenance: Woven fabrics often require less maintenance compared to knitted fabrics. They are less prone to snagging and unraveling, making them easier to care for and repair.
Knitting:
- Elasticity: Knitted fabrics have inherent elasticity due to the nature of the loops formed during the knitting process. This elasticity allows knitted fabrics to stretch and recover, making them comfortable for garments and accessories.
- Comfort: Knitted fabrics are often softer and more comfortable to wear compared to woven fabrics. The looped structure of knitted fabrics provides insulation and breathability, perfect for clothing items.
- Flexibility: Knitted fabrics are highly flexible and conform to the body’s shape. This flexibility makes them suitable for garments that require stretch and movement, such as activewear and swimwear.
- Pilling: One of the drawbacks of knitted fabrics is their tendency to pill. Pilling occurs when loose fibers cluster and create small balls on the fabric surface. However, with proper care, pilling can be minimized.
Conclusion:
When it comes to durability, both weaving and knitting have their strengths. Weaving provides stability, high tensile strength, longevity, and low maintenance. Knitting, on the other hand, offers elasticity, comfort, flexibility, and softness. The choice between weaving and knitting depends on the intended use and specific requirements of the fabric. Ultimately, understanding the characteristics of each technique can help in selecting the best technique for a particular application.
Comparison of Weaving and Knitting in Terms of Versatility
When it comes to versatility, both weaving and knitting offer unique advantages and possibilities. While weaving is known for its structured and precise technique, knitting offers a more flexible and varied approach. Here, we will explore the ways in which these two techniques differ in terms of their versatility.
Weaving:
Weaving involves the interlacing of warp and weft threads to create a fabric. This technique offers a high level of control and precision, allowing for intricate patterns and designs. Weaving is often used to create fabrics with distinct patterns and textures, such as tartans, plaids, and jacquard weaves.
However, weaving can be more time-consuming and labor-intensive compared to knitting. It requires a loom, which can be large and bulky, limiting the size of the fabric that can be created. Weaving is also generally more rigid, making it less suitable for stretchy or form-fitting garments.
Knitting:
Knitting, on the other hand, involves the creation of fabric by interlocking loops of yarn. This technique offers more flexibility and adaptability, making it suitable for a wide range of projects. Knitting allows for the creation of garments with stretch and drape, making it a popular choice for sweaters, scarves, and hats.
Knitting is often considered a more portable and accessible craft, as it does not require a large loom and can be easily done with just a pair of knitting needles. It also allows for experimentation and improvisation, as stitches can be easily added, removed, or modified during the creative process.
Comparison:
In terms of versatility, knitting tends to offer a broader range of possibilities compared to weaving.
- Design: Knitting allows for more intricate and complex designs, including lace and cables.
- Stretch and drape: Knitted fabrics have more stretch and drape, making them suitable for garments that require movement and flexibility.
- Portability: Knitting can be done anywhere and requires minimal equipment, making it a more portable option.
- Adaptability: Knitting allows for more flexibility in terms of modifying stitches and patterns during the creative process.
However, this does not mean that weaving is without its advantages. Weaving offers a level of precision and structure that is ideal for creating fabrics with distinct patterns and textures. It is often used in home décor items, such as rugs, curtains, and tapestries.
| Weaving | Knitting | |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Structured and precise | Flexible and adaptable |
| Cons | Time-consuming and labor-intensive | Less control over structure |
In conclusion, both weaving and knitting have their own unique advantages and possibilities. Weaving offers structured precision and is ideal for creating fabrics with distinct patterns, while knitting provides flexibility and adaptability, making it suitable for a wide range of projects. The choice between the two techniques ultimately depends on the desired outcome and personal preference.
Comparing Weaving and Knitting in Terms of Time Efficiency
Weaving and knitting are two popular textile techniques that have been used for centuries to create beautiful fabrics and garments. While both techniques have their own unique characteristics and advantages, one aspect that is often compared is their time efficiency. This article will explore how weaving and knitting differ in terms of the time it takes to complete a project.
Weaving
Process:
- Weaving involves interlacing threads or yarns at right angles to create a fabric.
- The process typically requires a loom, where the warp threads are held taut and the weft threads are woven through.
- Weaving can be done by hand or using mechanical or electronic looms.
Time Efficiency:
Weaving generally requires more time to complete a project compared to knitting. The process of setting up the loom and preparing the warp threads can be time-consuming, especially for complex designs. Additionally, weaving typically requires more precision and attention to detail, which can further increase the time it takes to complete a project.
Advantages:
- Weaving produces sturdy and durable fabrics that are less prone to stretching or losing shape.
- Complex patterns and designs can be easily achieved through weaving.
- Weaving can be more efficient for large-scale production.
Knitting
Process:
- Knitting involves creating fabric by interlocking loops of yarn.
- The process is typically done using two or more needles.
- Knitting can be done by hand or using knitting machines.
Time Efficiency:
Knitting is generally considered faster than weaving. The repetitive motion of creating each stitch allows for a quicker production process. However, the time it takes to complete a knitting project can still vary depending on the complexity of the pattern and the skill level of the knitter.
Advantages:
- Knitting allows for more flexibility and stretchability in the fabric.
- Knitted fabrics tend to be softer and more comfortable to wear.
- Knitting is more portable and can be easily done anywhere.
Conclusion
While both weaving and knitting have their own merits, in terms of time efficiency, knitting tends to be faster compared to weaving. However, it is important to consider other factors such as the desired fabric characteristics, complexity of the design, and the skill level of the crafter when choosing between weaving and knitting for a particular project.
FAQ:
What is the difference between weaving and knitting?
Weaving and knitting are two different techniques used to create fabric. The main difference between weaving and knitting lies in the process of interlacement of the yarns or threads. In weaving, two sets of yarns or threads, known as the warp and the weft, are interlaced at right angles to create a fabric. On the other hand, knitting involves creating loops with a single strand of yarn to form a fabric.
Which technique, weaving or knitting, produces a more durable fabric?
Both weaving and knitting can produce durable fabrics, but the durability may depend on the specific material used and the construction method. Generally, weaving creates a denser fabric that is less likely to stretch or lose its shape, making it more durable. Knitted fabrics, on the other hand, can be more prone to stretching and snagging, but this can be mitigated by using tighter stitches or using reinforcement techniques.
Which technique is more suitable for creating complex patterns and designs?
Both weaving and knitting can be used to create complex patterns and designs, but each technique offers different possibilities. Weaving allows for more precise control over the placement of individual threads, making it better suited for intricate patterns and detailed designs. Knitting, on the other hand, offers more flexibility in terms of creating textured patterns and incorporating various stitches. It also allows for easily creating three-dimensional shapes.
Are there any advantages of knitting over weaving?
There are several advantages of knitting over weaving. Firstly, knitting is generally faster than weaving, as it involves working with a single strand of yarn rather than interlacing multiple threads. Additionally, knitting allows for greater flexibility and stretchability in the resulting fabric, making it more suitable for creating garments that require a close fit or stretch. Knitted fabrics also tend to be softer and more comfortable against the skin.